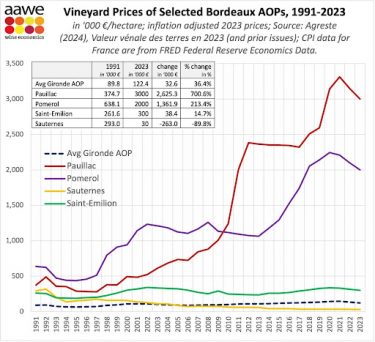
- Vineyard prices in Pauillac have risen over 700% in the last 30 years.
- Sauternes has faced a 90% decline during the same period.
- Pomerol has significantly outpaced Saint-Émilion, partly due to its compact size and luxury appeal.
The American Association of Wine Economists has released data on the evolution of Bordeaux vineyard prices from 1991 to 2023. Over this period, Bordeaux has become the centrepiece of a thriving, regulated wine investment market.
Global demand for Bordeaux wines has fueled remarkable growth, with top estates achieving iconic status as luxury brands. A 2011 valuation revealed that over 50 of Bordeaux’s leading châteaux belong to the €50 million club, with a combined market value exceeding €15 billion.
In the past two decades, Bordeaux fine wine prices have risen by an average of 200%, accompanied by significant increases in vineyard prices in its most sought-after appellations.
This article delves into the shifting dynamics of Bordeaux’s wine industry, examining their impact on vineyard prices and the contrasting trajectories of key sub-regions like Pauillac, Sauternes, Pomerol, and Saint-Émilion.
Pauillac’s extraordinary growth
Pauillac’s vineyard prices have experienced extraordinary growth over the past three decades, surging by 700.6% from €374,700 per hectare in 1991 to €3 million in 2023. The region is home to the First Growths Lafite Rothschild, Latour, and Mouton Rothschild.
When compared to other regions, Pauillac’s relatively small size – spanning approximately 1,200 hectares under vine – is a key factor contributing to its high vineyard prices. This limited vineyard area, combined with the prestige of its châteaux, creates a scarcity effect that drives up demand and valuation. Despite its compact footprint, Pauillac has managed to consistently dominate the fine wine market.
The rise of Pauillac aligns with the global increase in demand for fine Bordeaux wines, particularly during the 2000s and early 2010s, when new markets like China became major consumers. However, this growth has slowed in recent years. This could stem from market saturation, with collectors shifting their attention to other Bordeaux appellations or entirely different regions such as Burgundy and Champagne.
The decline of Sauternes
In stark contrast to Pauillac, Sauternes has suffered a decline, losing nearly 90% of its vineyard value since 1991. Once valued at €293,000 per hectare – higher than Saint-Émilion at the time – Sauternes vineyards are now priced at around €30,000 per hectare, according to AAWE. This fall can largely be attributed to waning consumer interest in sweet wines.
The production costs associated with Sauternes, which involve the labour-intensive process of harvesting botrytised (noble rot) grapes further compound the issue. While top producers like Château d’Yquem continue to uphold the region’s reputation, the broader market for Sauternes is facing challenges due to changing consumer preferences.
Pomerol and Saint-Émilion: a tale of two trajectories
Pomerol and Saint-Émilion present an interesting comparison, with Pomerol emerging as a high-growth luxury niche and Saint-Émilion maintaining steady performance. From 1991 to 2023, Pomerol vineyard prices rose by 213.4%, reaching €2 million per hectare, while Saint-Émilion saw only a modest 14.7% increase to €300,000 per hectare. These differences can be explained by several key factors.
- Size and scale
Saint-Émilion spans a vast 5,400 hectares, compared to Pomerol’s much smaller 800 hectares. This sheer scale means Saint-Émilion includes a wide range of producers, from elite châteaux like Cheval Blanc and Ausone to lesser-known estates producing more affordable wines. In contrast, Pomerol’s compact size results in a higher concentration of prestigious vineyards, with fewer smaller players to dilute its overall market perception.
- Classification systems
Saint-Émilion’s classification system – updated every decade – categorises its estates into tiers such as Premier Grand Cru Classé A and B, and Grand Cru Classé. However, the frequent use of the “Grand Cru” designation (applied to over 60% of the region’s wines) might work against it, and partly diminish the exclusivity of this title.
Conversely, Pomerol lacks any formal classification system, allowing individual estates like Pétrus and Le Pin to dominate through their reputations alone. This lack of stratification has paradoxically bolstered the region’s image as a luxury appellation. Its reputation as a source of small-production, Merlot-dominant wines has further cemented its status as a ‘cult’ appellation among collectors and investors.
- Smaller players and price dilution
Saint-Émilion’s large number of smaller, lesser-known producers contributes to its lower average vineyard price. These producers often operate outside the Grand Cru Classé system, pulling down the overall valuation of the region. In Pomerol, the scarcity of vineyards and the dominance of high-profile estates create a ‘halo effect’ that supports consistently high valuations, even for lesser-known properties.
Implications for the wine investment market
The contrasting trajectories of Bordeaux’s appellations highlight the complexity of the fine wine investment market. Pauillac’s recent plateau demonstrates that even the most prestigious regions are not immune to market saturation, while Pomerol’s steady growth underscores the enduring appeal of scarcity and exclusivity. In contrast, Sauternes illustrates the vulnerability of regions reliant on shifting consumer preferences. However, renewed efforts by producers to embrace sustainability, innovation, and rebranding may help revive interest in sweet wines and mitigate some of these challenges.
Despite fluctuations, Bordeaux’s iconic estates and global reputation remain a cornerstone of the fine wine market. For investors and collectors, navigating the nuanced landscape of vineyard prices and evolving market dynamics will be crucial to securing long-term success in this ever-changing industry.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today