- As an internationally traded asset, fine wine is affected by economic and political factors including trade wars and tariffs.
- Demand for certain wines and regions can shift as tariffs directly impact pricing, availability and liquidity.
- Diversification and strategic investment are key to navigating the fine wine market amid trade wars and tariffs.
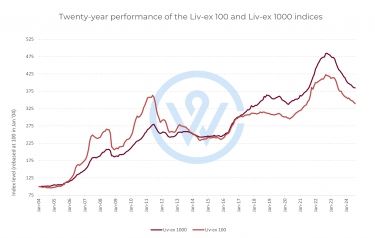
Over the past two decades, fine wine has transitioned from a luxury product to a well-established internationally traded investment asset. Like any asset enjoying global demand, fine wine is subject to the economic and political forces that shape international trade.
Legislative decisions, such as changes in taxation and import duties, can directly impact its pricing and accessibility. Trade wars, tariffs, and protectionist policies further add layers of complexity, affecting demand, market stability, and ultimately, investment returns. This article explores how these trade factors influence the fine wine investment market and what investors need to consider.
How trade wars affect wine demand and pricing
Trade wars often involve the imposition of tariffs or import duties on goods traded between countries, which can create a ripple effect across industries and markets. When tariffs are imposed on wine, they can create price volatility, limit access to certain markets, and reduce liquidity, which can impact the investment performance of the affected wines and regions.
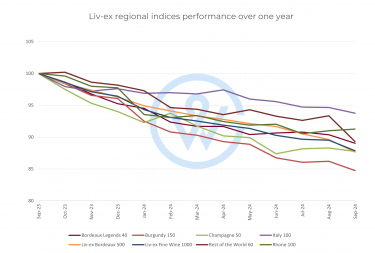
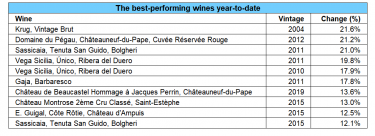
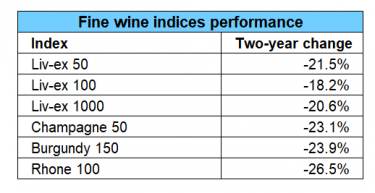
For example, in the ongoing trade tensions between the United States and the European Union, wine has frequently been a target for tariffs. In 2019, the USA imposed a 25% tariff on certain European wines in response to a dispute over aircraft subsidies. This tariff included wines under 14% alcohol, impacting popular wine-producing regions such as France, Spain, and Germany, but excluded Champagne and Italy. As a result, Champagne and Italy took an increased market share in the US; when the tariffs were lifted, Bordeaux and Burgundy enjoyed an immediate uptick.
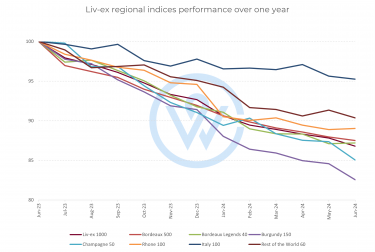
Market impact of the 2019 US tariffs on European wine: In 2019, Bordeaux accounted for 48% of the US fine wine market on average, according to Liv-ex. From October 2019 to the end of 2020, Bordeaux’s average share of US buying fell to 33%. Burgundy’s share also declined – from 13% before the tariffs to 8%. Conversely, demand for regions exempt from the tariffs rose significantly during this time. Champagne rose from 10% to 14%, Italy from 18% to 25% and the Rest of the World from 4% to 10%. Regions exempt from the 25% US tariffs also saw the biggest price appreciation in 2020. For the first time on an annual basis, Champagne outperformed all other fine wine regions. This led to its global surge.
Market impact of the 2020 Chinese tariffs on Australian wine: In 2020, China imposed tariffs on Australian wine amid a series of blows to Australian exports, which had a profound impact on Australia’s budding secondary market. Since the tariff introduction, prices for some of the top wines dipped, creating pockets of opportunity. For instance, the average price of Henschke Hill of Grace fell 4%, while Penfolds Bin 707 went down 9%. Since the tariff suspension earlier this year, Australian wine is coming back into the spotlight.
When it comes to pricing, tariffs can drive up the end cost of imported wine, particularly impacting markets where fine wine demand is driven by consumers with limited domestic alternatives. When tariffs make imported wines prohibitively expensive, consumers may turn to other regions or domestic products.
From an investment perspective, the unpredictability of trade policies requires a strategic approach that accounts for potential regulatory changes in key markets.
Strategic wine hubs in tariff-influenced markets
In response to tariffs, some regions have positioned themselves as strategic wine trading hubs by offering tariff-free or reduced-tariff environments for wine trade. Hong Kong, for example, abolished its wine import duty in 2008, aiming to become the “wine trading hub” of East Asia.
This decision has proven instrumental for the fine wine market in Asia, as investors from mainland China and other countries can access European wines without the additional costs that would apply if purchased domestically. As a result, Hong Kong has emerged as a leading location for wine auctions and a key destination for collectors and investors in Asia.
The role of trade agreements
For regions with established wine industries, trade agreements and economic alliances play a significant role in shaping wine tariffs and market access. The European Union, for instance, has trade agreements with multiple countries, allowing for reduced tariffs on wines imported from places like Australia and Chile. However, Brexit has introduced new complexities, as the United Kingdom – one of the largest fine wine markets – now operates independently from the EU.
For investors navigating the fine wine market amid trade wars and tariffs, diversification and strategic storage are essential. Diversifying across different wine regions and vintages can help minimize exposure to trade barriers affecting specific countries.
Additionally, storing wine in bonded warehouses can mitigate the risk of sudden tariff impositions on wine imports, preserving the asset’s value. Monitoring geopolitical developments is also crucial, as policy shifts can happen quickly and have immediate effects on wine prices.
While trade wars and tariffs present complexities, they also create opportunities in the fine wine investment market. In a politically charged landscape, understanding the influence of trade policies on wine markets is critical. By staying agile and responsive to policy changes, investors can better navigate the complexities of wine investment in a globalised yet fragmented market.
Want to learn more about fine wine investment? Download our free guide.