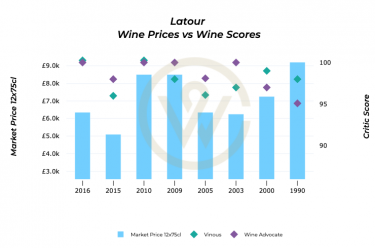
Discover how wine critics influence Bordeaux wine investment in 2025 and whether Robert Parker’s legacy still shapes today’s market.
Provenance, a good vintage, scarcity, and brand are all factors that influence the price of fine wine, and hence the world of wine investment. Another factor that has, traditionally, impacted wine value is the critic. A top score can inspire confidence in the price performance of a wine, while an unfavourable rating can have the opposite effect.
However, is the role of the wine critic as important as it was in the past? With the retirement of the hegemonic world-renowned wine reviewer, Robert Parker, who helped put Bordeaux, California and the Rhône at the forefront of wine buyers’ minds, and the rise of digital media, what does the future hold?
WineCap met figures from leading Bordeaux estates for their insights into the place of wine criticism in 2025 and the years ahead. In Part I, we discuss the legacy and the evolving role of the wine critic.
- Robert Parker’s era of singular influence is over – today’s wine criticism is a collective effort.
- Critics still shape wine investment decisions, but their role is now one of many in a more democratic media landscape.
- The rise of digital voices and ‘wine educators’ is expanding access and perspective in the fine wine world.
Wine criticism in transition: legacy vs digital influence
Several producers saw formal wine criticism as a keystone of information for customers, but also recognised that it was part of a developing media ecosystem largely because of the impact of the internet.
Château Valandraud, Premier Grand Cru Classé B, Saint-Émilion
Jean-Luc Thunevin, owner of Château Valandraud, thinks the importance of the traditional wine critic remains important for his château as the legacy of Robert Parker endures.
‘Parker had a hegemonic position; that is, he represented 80% of global influence. Today, in any case, there are collaborators who worked for him, who are very talented and who, two or three years ago, represented Parker’s influence,’ Thunevin told WineCap. ‘We can say that today, when you are a wine merchant, we use five or six major journalists, and we get an idea of what the wine is worth.’
Château Cheval Blanc, Saint-Émilion
‘In terms of the impact of the wine critics on the fame of our wines, we are very respectful of the job of the critics,’ Pierre-Oliver Clouet, technical manager at Château Cheval Blanc, explained. ‘We produce wine, there are wine distributors there to distribute the wine, there are wine collectors that collect the wine, and there are wine critics, who have to critique the wine. So, everybody has their own job in the wine world.’
The vast and varied selection of wine makes the role of the critic key, with Clouet adding that ranking wine estates, vintages, appellations, countries, and regions is important for consumers.
‘The impact of critics is so important for the final client because the number of wines available on the market is huge. You have to find the critique who has your taste, and you have to follow him or her. This is the job: to help the consumer, to know more about what they’re going to purchase’.
Château Clinet, Pomerol
Ronan Laborde, managing director and owner at Château Clinet, is adamant that professional criticism is still an important fixture in the wine world, but acknowledges that information is more accessible to collectors and laymen alike today than in decades past. ‘We still need wine critique. When Robert Parker was reviewing and ranking, there was less wine criticism, and the web was not so widespread. Nowadays, there continue to be a lot of highly respectable wine critics.’
Laborde added that clients also have opportunities to bolster critic ratings with their own first-hand experience. ‘There are a lot of people who are really interested in wine and have the chance to visit wineries, taste the wines, and import the wines. So, it’s easier nowadays to try and have your own opinion than before. Robert Parker was a reference at the time he was active, but nowadays, it’s more split.’
Wine critique landscape in 2025: complexity and change
Château Margaux, First Growth, Haut-Médoc
Philippe Bascaules, managing director at Château Margaux, had an open-minded perspective on the shifting, changing, landscape of wine critique, not jumping to any conclusive opinion on its direction for the time being.
‘We are in a time when it’s very difficult to know the direction of journalists and social media and all this new communication, and how the consumers will use all of it to buy wine,’ he said. ‘Of course, it used to be so simple. Today, it’s much more complex and I think probably it’s even a good evolution, I would say, because then it can be a little bit more diverse, and everyone can find his own advisor. I think we are in transition and will know later exactly where it will lead and what it will mean.’
Château Coutet, Premier Cru, Sauternes
Other producers echo this sentiment. At Château Coutet, marketing director Aline Baly appreciates the rise of ‘wine educators’ who help spread awareness about lesser-known properties.
‘In the last decade, we’ve seen a lot of new wine critics, or I also like to call them “wine educators” because they’re helping us get the message out there,’ marketing director Aline Baly told WineCap. ‘Some of the vineyards in this region are very tiny. We can’t be everywhere. We can’t be travelling and opening our wines and describing these wines. So, the wine critics, or wine educators help us get the message out.’
Regarding the growing number of critics, Baly was enthusiastic. ‘There is definitely a change from having very few people who are the spokespeople for all the vineyards in the world to a larger group of individuals who’ve come to visit, who’ve tasted wines and helped us get the message out there.’
Why wine critics still matter: education and expertise
Château Calon-Ségur, Third Growth, Saint-Estèphe
‘At the time of the Primeurs, we host many journalists from France and around the world,’ general director and owner of Château Calon-Ségur Vincent Millet said. ‘Today we have about fifteen journalists who come to taste the Primeurs every year. But what is also interesting is that these are the same journalists who will taste the wines when they are bottled, or a few months after bottling. So, they have a vision of a very young wine and a wine that has been aged in barrels, as well as a few months after bottling.’
This educational insider experience was invaluable for consumers, he added. ‘Today, what is interesting to see is that journalists have a culture of wine, follow the properties, follow the history of the property, and in some ways, these same journalists become true authorities on our wines. Even if we work with the brokers and merchants, the consumer will still look at the notes and comments of these same journalists. It is important for us to be able to explain how we work and what our philosophy is so that journalists can better understand the wines when they taste them’.
From Parker to pluralism: collective influence in wine
Several producers agree: the days of one critic dominating the wine conversation are behind us.
Château Pichon-Longueville Baron, Second Growth, Pauillac
‘I don’t think that we will ever again see one critic have such a completely dominant position as Robert Parker had. It was an accident of history in many ways. He just started at the right time, in 1982, when America was discovering the great wines of Bordeaux, and became accepted as the utterly reliable guide that he was,’ explained Christian Seely, managing director of AXA Millésimes, owner of Pichon-Baron.
‘Today, there are many talented wine tasters and critics, and I think that it’s more of a collective influence. So, there will be perhaps a dozen really major critics who move the market, and I think on a collective basis, this is actually a much healthier thing. I think that for one person to have so much influence was probably slightly unbalanced and dangerous. These days, you can choose, as a consumer, from a number of very good critics and decide which ones you like best and follow them.’
Château La Mondotte, Premier Grand Cru Classé, Saint-Émilion
‘The time of the likes of Robert Parker is completely finished,’ said owner of Château La Mondotte Stéphane von Neipperg. ‘Now we will have perhaps five to ten well known wine critics for the consumer. So, it will be a much more open game. Parker was an important guy because he made what makes a good wine understandable for a lot of people. However, it is also good to have different opinions.’
Von Neipperg pointed to the 2021 vintage as an example of how critic viewpoints can vary significantly, supporting his view of the benefits of such diversity. ‘If you read about the ratings of 2021, there were sometimes five to ten points difference for the same wine.’
As Bordeaux and the broader wine world evolve, so too does the role of the critic – moving from singular gatekeeper to a chorus of trusted voices, guiding collectors, investors, and enthusiasts through an increasingly nuanced landscape.
See also our Bordeaux I Regional Report.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine.
Start your wine investment journey with WineCap’s expert guidance.



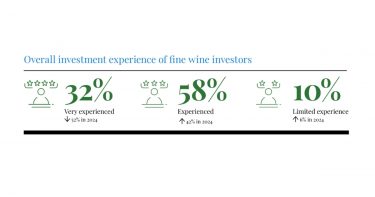 *UK
*UK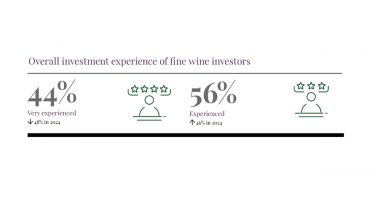 *US
*US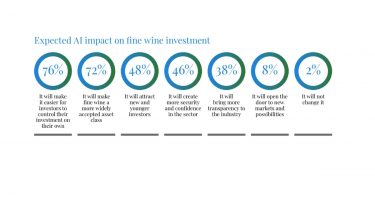 *UK
*UK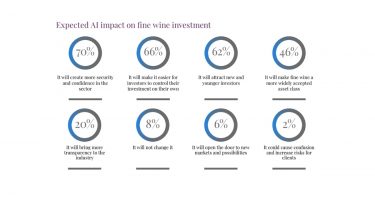 *US
*US