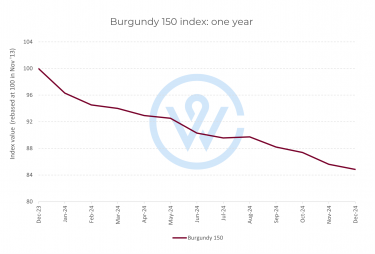
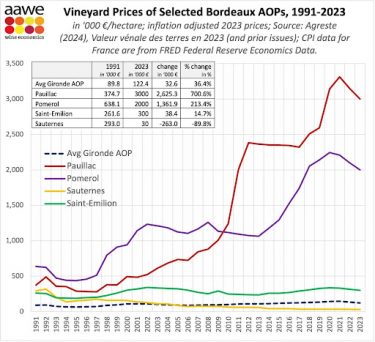
Burgundy is one of the world’s most revered and historically significant wine regions. For centuries, it has captivated collectors and wine lovers with its ability to express terroir more precisely than almost anywhere else on earth. Understanding the regions in Burgundy is essential to understanding why it produces some of the most sought-after fine wines in the world.
Unlike larger wine regions defined by broad styles or dominant producers, Burgundy is a mosaic of tiny appellations, historic villages, and meticulously delineated vineyard parcels. Here, value, quality, and reputation are shaped not by château names, but by vineyard location, soil composition, and microclimate. This is a region where a few metres of land can dramatically change a wine’s character – and its price.
At the heart of Burgundy’s complexity lies its regional structure. While thousands of climats and individual vineyards exist, the region is fundamentally organised into five core Burgundy wine regions, each contributing something distinct to Burgundy’s identity. From the cool, mineral-driven whites of Chablis to the warmer, expressive wines of the Mâconnais, these regions together form one of the most intricate wine landscapes in the world.
Regions in Burgundy: structure
Geographically, Burgundy forms a long, narrow corridor of vineyards running from north to south through eastern France. It is divided into four contiguous regions and one satellite region, each with its own climate, soils, and stylistic identity.
Although Beaujolais is sometimes associated with Burgundy through tradition and grape variety, administratively it belongs to the Rhône and is not considered part of Burgundy’s official wine regions.
Burgundy’s vineyard area totals approximately 30,000 hectares, with more than 80% classified under the AOC system. Despite producing only around a quarter of Bordeaux’s volume, Burgundy’s influence on the fine wine market is disproportionately large. Its emphasis on scarcity, site specificity, and classification has made it a benchmark for quality worldwide.
Chablis (Satellite)
Located just two hours southeast of Paris, Chablis is Burgundy’s northernmost outpost and one of the world’s great sources of white wine. Unlike the rest of Burgundy, Chablis sits geographically apart from the Côte d’Or, forming a satellite region with a distinct climate and geological identity.
Chablis produces wines exclusively from Chardonnay grapes, yet its style is markedly different from the richer whites of the south. This is largely due to its Kimmeridgian limestone soils, formed from an ancient seabed rich in fossilised marine life.
Characteristics of Chablis wines
Chablis wines are renowned for their:
Cool continental temperatures preserve acidity, giving Chablis its linear structure and precise expression.
Appellations of Chablis
Chablis is divided into four hierarchical appellations:
-
Petit Chablis
-
Chablis
-
Chablis Premier Cru
-
Chablis Grand Cru
The Grand Cru vineyards – just seven climats clustered along the Serein River – represent one of Burgundy’s smallest and most prestigious fine wine zones. Premier Cru sites such as Vaillons, Montmains, Fourchaume and Vaulorent also play a crucial role in defining Chablis’ quality hierarchy.
Côte de Nuits: the heart of Pinot Noir
The Côte de Nuits forms the northern half of the Côte d’Or and is widely regarded as the spiritual home of the world’s greatest Pinot Noir. This narrow strip of east-facing limestone slopes produces some of the most expensive and sought-after red wines on earth.
Key villages include Gevrey-Chambertin, Morey Saint-Denis, Vosne-Romanée, Chambolle-Musigny, and Nuits-Saint-Georges. The region is also home to the most iconic Burgundy estate of all: Domaine de la Romanée-Conti.
Monastic origins and vineyard classification
Viticulture in the Côte de Nuits dates back to Roman times, but it was Benedictine and Cistercian monks who laid the foundations of Burgundy’s modern vineyard system during the Middle Ages. Through centuries of observation, they identified which vineyard parcels consistently produced superior wines, giving rise to the concept of climats and, eventually, grand cru vineyards.
Côte de Nuits Grand Crus
Some of the world’s most revered grand crus are located here, including:
-
Chambertin
-
Clos Saint-Denis
-
Clos de Vougeot
-
Échézeaux
-
Richebourg
-
Romanée-Conti
-
La Tâche
These wines command extraordinary prices due to their rarity, tiny production levels, and global demand. Even in weaker market cycles, Côte de Nuits grand crus remain among the most liquid assets in fine wine.
The Côte de Nuits forms the northern half of the Côte d’Or and is the spiritual home of the world’s greatest Pinot Noir. This narrow strip of hillside produces some of Burgundy’s most celebrated bottles – home to legendary appellations like Gevrey-Chambertin, Morey Saint-Denis, Vosne-Romanée, and the most iconic estate of all, Domaine de la Romanée-Conti.
Côte de Beaune: elegance, balance and great white wines
The Côte de Beaune forms the southern half of the Côte d’Or and is centred around the historic town of Beaune, the commercial heart of Burgundy. This region is unique in producing both exceptional red and white wines, with a stronger emphasis on Chardonnay than its northern neighbour.
A region of diversity
Before the introduction of the AOC system in 1936, wines from this area were broadly referred to as “Beaune wines.” Today, the Côte de Beaune encompasses a complex patchwork of villages, Premier Cru climats, and celebrated grand cru sites.
Iconic appellations include Puligny-Montrachet, Chassagne-Montrachet, Meursault, and Aloxe-Corton. White wines from grand cru vineyards such as Corton-Charlemagne and Montrachet are widely considered among the finest Chardonnay expressions in the world.
The Côte de Beaune contains more than 40 Premier Cru climats, producing wines prized for their balance, structure, and ageing potential.
Côte Chalonnaise: value and tradition
Situated south of the Côte de Beaune, the Côte Chalonnaise is often overlooked yet it plays a vital role in Burgundy’s ecosystem. The region produces high-quality wines from Pinot Noir, Chardonnay, and Aligoté, often at more accessible price points than the Côte d’Or.
Notable appellations of the Côte Chalonnaise
Key villages include:
-
Mercurey
-
Givry
-
Rully
-
Montagny
These appellations offer excellent value while maintaining Burgundian character. Historically, the Côte Chalonnaise also played a key role in the development of Crémant de Bourgogne, with early sparkling wine production centred around Rully and Mercurey.
Mâcconais: warmth, fruit and approachability
The Mâconnais is Burgundy’s southernmost wine region, defined by rolling hills, warmer temperatures, and dramatic limestone formations. Monastic orders, particularly the Abbey of Cluny, were instrumental in establishing viticulture here as early as the 10th century.
Wine styles and grape varieties
Around 80% of vineyards are planted to Chardonnay, producing wines that are generally riper and more fruit-forward than those of northern Burgundy. The region also grows Gamay and smaller amounts of Pinot Noir.
Notable regional appellations include:
-
Pouilly-Fuissé
-
Pouilly-Vinzelles
-
Saint-Véran
-
Viré-Clessé
These wines consistently offer strong quality and value, making the Mâconnais an increasingly important region for collectors seeking Burgundy character without Côte d’Or pricing.
Final thoughts on Burgundy wine regions
Burgundy’s complexity is not a barrier – it is its greatest strength. From the steely minerality of Chablis to the haunting depth of Vosne-Romanée and the crystalline precision of Puligny-Montrachet, each region offers its own interpretation of Pinot Noir and Chardonnay.
Together, these Burgundy wine regions form one of the most intellectually rewarding and historically rich wine landscapes in the world. Defined by centuries of observation, monastic influence, and an unparalleled focus on terroir, Burgundy continues to set the global benchmark for fine wine – captivating collectors, investors, and wine lovers alike.
Looking for more? Read our Burgundy Regional Report, which delves into the fundamentals of this fascinating region and the development of its investment market.