Alternative assets are investments outside traditional stocks and bonds. These can range from property, private credit and venture to collectibles such as fine wine, art, watches and classic cars. In 2025, fine wine stands out for its low correlation with equities, global demand, finite supply, strong brands, and the ability to build diversified portfolios from blue-chip regions such as Bordeaux, Burgundy, Tuscany, Piedmont, and Champagne. Success comes from rigorous selection, professional storage, long investment horizons (5-10+ years), and data-driven decision making.
What are alternative assets – and why they matter in 2025
Alternative assets cover three broad categories:
- Collectibles: fine wine, whisky, art, classic cars, watches, rare coins.
- Private markets: private equity & credit, venture capital, real estate, infrastructure.
- Hedge strategies: market-neutral, macro, commodities, and other absolute-return approaches.
The Chartered Alternative Investment Analyst Association (CAIA) frames “alternatives” by their limited liquidity, pricing opacity, and non-traditional risk/return drivers compared with public markets.
Why diversification with alternative assets matters
Many alternatives move differently from listed equities and bonds, which means they can dampen portfolio swings when traditional markets are volatile.
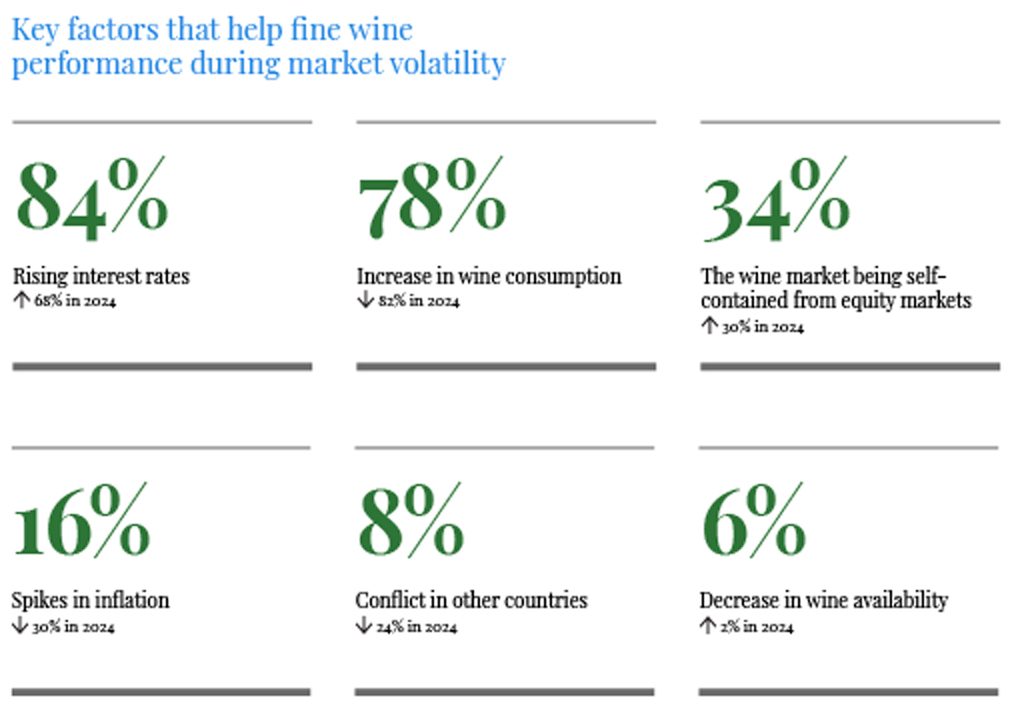
Fine wine is a strong example. Studies have shown it has low – and sometimes negative – correlation with equity markets, improving portfolio efficiency when included alongside traditional assets. In 2025, demand for fine wine has risen by 16% due to its independence from mainstream financial markets. Notably, 34% of UK wealth managers now cite wine’s self-contained nature as a key factor in its resilience during periods of market volatility, up from 30% in 2024.
Hedge funds aim for the same goal: delivering returns that aren’t tied too closely to market cycles. In 2024-25, hedge fund results have varied across strategies, but overall performance has improved, highlighting their role as diversifiers rather than trackers of stock indices.
Alternative assets and inflation
One of the strongest advantages of alternative assets is their ability to preserve purchasing power when inflation erodes the value of money. Unlike fixed-income instruments, where interest payments may lag rising prices, many alternatives are underpinned by tangible scarcity and global demand, which supports value through inflationary cycles.
- Private real assets such as infrastructure and opportunistic real estate have historically passed on rising costs more effectively than their listed counterparts, offering stronger inflation protection.
- Collectibles benefit from their finite nature. The OIV reported 2024 global wine production at a near 60-year low, underlining how supply limits create pricing power. Fine wine is particularly resilient here: each bottle consumed makes the remaining stock rarer, while global demand ensures international relevance. Over time, well-stored vintages not only hold their value but often appreciate at a pace that outstrips inflation, similar to how gold is viewed as a store of value.
- Art and luxury goods also serve as currency diversifiers. While the global art market saw values contract by 12% in 2024, activity levels remained robust, showing continued demand for tangible assets that trade across currencies and borders.
In effect, alternatives hedge inflation in ways traditional portfolios cannot. By anchoring value in scarcity, durability, and global liquidity, they help investors preserve real wealth.
Why timing and selection are important
Alternative assets do not present a uniform return stream, and fine wine illustrates this better than most. Outcomes differ dramatically depending on region, producer, vintage, and even release timing. Burgundy, for instance, can respond to very different dynamics than Bordeaux, while Champagne and Tuscany follow their own cycles. Within each region, a benchmark producer may hold value through downturns while lesser names fade.
Even within a single estate, the vintage effect is powerful: the release prices and the performance of First Growth Bordeaux shows a wide gap between celebrated vintages like 2000 or 2009 and those considered ‘off’ years. Variables like provenance and storage, widen the gap further.
Just as in private equity or hedge funds, where manager selection drives returns, in the fine wine market, knowledge and timing are decisive.
How liquid are alternative assets?
Liquidity in alternative assets differs from mainstream markets. Public equities and bonds trade daily on exchanges with instant settlement. By contrast, most alternatives – whether private funds or fine wine – take longer to change hands. A sale depends on finding a buyer, agreeing on price, and, in some cases, waiting for a trading window.
This slower pace can be advantageous. Investors willing to commit capital for longer are often rewarded with an extra return for patience. In fine wine, the best opportunities often come from holding rare vintages through periods of scarcity, then releasing them to market when demand peaks.
Access, however, is improving. Just as private credit has grown through evergreen and interval funds, fine wine platforms now make trading more efficient and transparent. Still, liquidity remains uneven: blue-chip Bordeaux or Burgundy may find a ready market, while niche producers or lesser vintages can take longer to sell.
The role of fine wine in 2025
Among alternative assets, fine wine stands out. In 2025, for the third year in a row, it came on top as the most in-demand collectible among financial advisors and wealth managers in both the UK and US. Fine wine is a viable alternative investment avenue for the following reasons:
- Scarcity meets demand: Production is both finite and shrinking, while rising global wealth continues to fuel steady demand.
- Global and brand-driven: Iconic names such as Lafite Rothschild, DRC, and Salon are recognised worldwide and have a track record of delivering consistent value.
- Diversifiable: Unlike art or cars, fine wine offers broad exposure across regions, producers, and vintages. With hundreds or thousands of cases produced each year, valuations are more transparent and portfolios easier to build.
- Historically resilient: Fine wine has shown stability in market downturns and attractive long-term returns. Investors can track the performance of individual labels – or entire portfolios – directly through Wine Track.
In 2025, alternatives are no longer niche: they are central to how sophisticated investors diversify, preserve wealth, and seek differentiated returns. Fine wine brings together the key qualities that define successful alternatives: tangible scarcity, global demand, and return dispersion that rewards knowledge and timing.
Fine wine investment FAQs
Is fine wine a good hedge against inflation?
It can help preserve purchasing power over multi-year horizons due to finite supply and global demand, but outcomes vary. Diversify and keep realistic horizons.
How much do I need to start?
You can build a credible, diversified starter portfolio with a five-figure GBP budget; larger allocations allow more breadth and depth.
How long should I invest for?
Plan for 5-10+ years to capture ageing-related scarcity and demand. Tactical positions may realise sooner.
Where should I store wine?
In bonded, climate-controlled facilities with full insurance and documented chain of custody.
What returns should I expect?
Returns are not guaranteed. Focus on selection quality, costs, and disciplined process.


