- The market for alternative investments has seen robust growth owing to burgeoning demand for non-traditional assets.
- Alternative assets offer a hedge against inflation, and often provide investors with higher returns.
- Some of the main challenges when it comes to alternative investments are accurate valuations and liquidity.
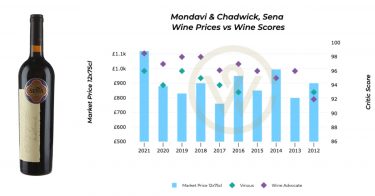
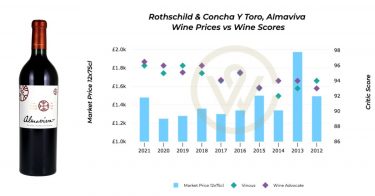
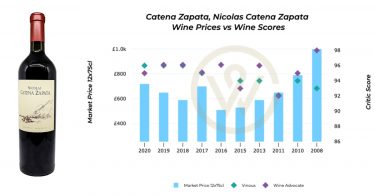
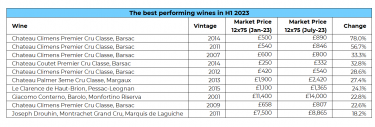
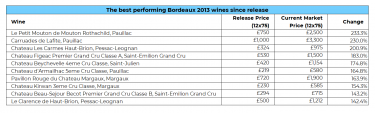
Alternative investments, those that fall outside traditional financial assets like stocks, bonds, and cash, have garnered immense popularity among affluent investors. From classic cars and luxury handbags to fine art, these assets represent both a passion and a store of value. According to the results of our global wealth management survey, fine wine emerged as the most in-demand passion asset. This article explores the burgeoning market for alternative investments, with a special emphasis on fine wine, contrasting and comparing their attributes, risks, and potential.
Alternative investment landscape
Alternative investments, often tangible assets, are known for their rarity, craftsmanship, and cultural relevance. Watches, luxury bags, art, whisky, and fine wine fall under this category, offering diversification for investment portfolios.
The market for alternative investments has witnessed robust growth owing to rising global wealth and a burgeoning demand for non-traditional assets. According to Richard Bacon, Head of Business Development at Shard Capital, ‘in the last two years there has been a tangible increase in how accessible and democratized these assets have become’.
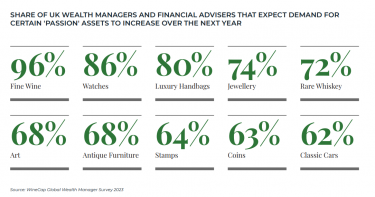
As traditional markets have faced increased volatility, clients have turned to passion assets to safeguard their wealth. Economic uncertainty and inflation have fuelled interest, as these assets tend to retain value over time and provide investors with higher returns outside of their traditional portfolios.
This can be noted in the performance of the luxury goods market, which posted a record year in 2022, reaching a market value of €345 billion, despite geopolitical tensions and macroeconomic uncertainty. This momentum persisted into the first quarter of 2023, achieving 10% growth over 2022, according to Bain & Company.
The luxury group Louis Vuitton Moët Hennessy (LVMH), which owns Champagne houses Moët & Chandon, Dom Pérignon, Veuve Clicquot, Krug, Ruinart and Mercier, also had a record year in 2022, and reported a 15% growth in the first half of 2023.
Alternative assets compared
While alternative investments have enjoyed growing popularity, each asset class operates by its own market dynamics. There are some notable differences and similarities, for instance, between fine wine, art and luxury goods. Below we outline some of the differences.
Investment nature:
- Fine wine: A consumable and perishable asset produced in multiple quantities (vintage-dependent) with value appreciation due to age, supply-demand and quality.
- Art: A unique, non-perishable asset, valuing subjectivity and aesthetic appeal.
- Luxury goods: Tangible assets like watches and bags, offering functional utility and value based on brand prestige and condition.
Value determinants:
- Fine wine: Producer reputation, age, rarity, condition, critic scores.
- Art: Artist reputation, uniqueness, historical significance, and condition.
- Luxury goods: Brand reputation, craftsmanship, condition, and rarity.
Risks:
- Fine wine: Market fluctuations, storage conditions, and provenance verification.
- Art: Market trends, authenticity, and condition degradation.
- Luxury goods: Counterfeiting, fashion trends, and wear and tear.
However, all these assets share common grounds, including tangibility, scarcity and uniqueness driving value, a strong connection to culture and lifestyle, and being a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty.
Market challenges and opportunities
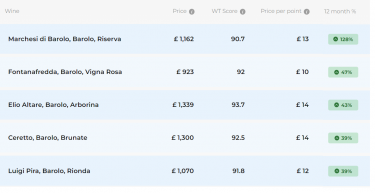
Some of the main challenges when it comes to alternative investments are valuations and liquidity. Some assets may need longer time to trade compared to traditional investments. Values may fluctuate based on trends, and condition. It is often harder to value a single piece of art accurately, compared to fine wine, which is often made in significant quantities and cases regularly trade internationally.
The main opportunities in the alternative investment market are diversification, their potential for appreciation and pleasure and fulfilment beyond the monetary benefits. Alternative assets offer a balanced and diversified portfolio, mitigating risks from traditional markets. Meanwhile, rarity and cultural significance can result in substantial value appreciation. Beyond financial rewards, these investments offer emotional and aesthetic satisfaction. Navigating the market for alternative investments requires an understanding of the underlying dynamics, diligent verification, and a discerning eye for value.
To find out more about fine wine as an alternative investment, download our special report below.