A version of this article written by WineCap’s CEO Alexander Westgarth was first published by Forbes.
- A popular alternative investment, fine wine can plug the gaps left by struggling assets, helping to steady and raise performance across a whole portfolio.
- As a tangible asset, fine wine delivers stability in uncertain times.
- Part of the rising demand for fine wine can be attributed to environmental factors.
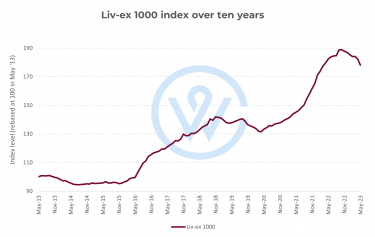
Between April 2020 and September 2022, the average bottle of fine wine rose 43.5% in value. While the fine wine market has dipped and corrected since, the general trajectory has historically pointed upwards.
Since 2004, Liv-ex data shows that the average bottle price tag has risen by 329.9%. While it can be a good investment, better still, fine wine is a great means to plug the gaps left by struggling assets, helping to steady and raise performance across a whole investment portfolio. Earlier this year, WineCap conducted a survey where we found that 92% of U.S. wealth managers believe demand for fine wine will increase over the next year. This is for three main reasons, and below we outline how to best take advantage of this asset’s potential for stability, sustainability and profitability.
Stability in uncertain times
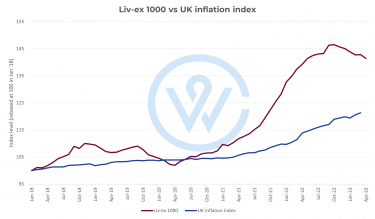
We live in uncertain times. In the last year, businesses have had to cope with rocketing energy bills, inflation and interest rates. In times of hardship, people want something solid. This is why tangible assets like property, gold or fine wine tend to feel more precious during market downfalls. WineCap found that 56% of wealth managers invest in wine to add stability to portfolios across different market conditions.
It is not only wine. Across the entire investment landscape, there is an increased demand for reliability. In the past few months, gold prices have been rallying too. When the gold prices go up, this often indicates that investors are looking to preserve their wealth and shield it from market shocks.
At the same time, investors have been shying away from bullish investments like technology stocks. Apple, for example, has suffered significant dips. Microsoft shareholders have endured wobbly turbulence (though, at the time of this writing, the company is beating financial expectations). Likewise, the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite has been on a rocky ride over the past months.
As the choppy waters continue, many investors want steady ships to ride out the storm – not fancy speedboats. With its historically low volatility, fine wine delivers just that. Unlike stocks or bonds, fine wine prices do not tend to fluctuate massively as the market operates with its own dynamics. Regions like Champagne are currently seeing high levels of demand, not only because of the quality of the wines but the stability the region has historically offered.
Similarly, wines from Bordeaux, Tuscany and the Rhône may be more solid. However, not all fine wines are made the same. Extremely rare and highly coveted wines from Burgundy, for instance, can make a great investment but remain a riskier asset if stability is what you are after.
Demand for environmentally friendly assets
Our survey also found that investors are prioritising environmentally friendly assets, and 56% say they invest in fine wine because it is a sustainable asset class with a low carbon footprint. This trend is hardly surprising; 2023 has been the hottest summer on record.
Dozens of wildfires are actively blazing through the USA. Meanwhile, elsewhere, the excess water caused by melted ice caps means that flooding and torrential rains are washing away entire communities. In August, flash floods tore through Pennsylvania, killing five people. Naturally, investors are keen to put their money into assets that will mitigate some of the climate risks.
Part of the interest in fine wine can be attributed to environmental factors. Vines promote healthy soil quality and nourish pollinators, which are essential for biodiversity. A hector of vineyard soaks up a respectable 2.84 tonnes of carbon every year. The best winemakers use age-old sustainable practices. Many will even opt for a pony and cart rather than disturb the terrain with a tractor.
Some well-known organic producers include Burgundy’s Domaine Leflaive and the Bordeaux Fifth Growth, Château Pontet-Canet. While not officially certified, Burgundy’s Domaine de la Romanée-Conti also follows organic and biodynamic guidelines. Meanwhile, some producers are reducing bottle weight in pursuit of sustainability such as Burgundy négociant Albert Bichot, which has reduced the weight of their bottles from around 700 grams to 450 grams.
Climate-conscious investors can keep an eye out for wineries investing in a greener future.
Strong returns
According to our survey, almost half of the investors choose fine wine because they want strong returns. Historically, fine wine has offered generous returns over long periods without sacrificing quality or environmental qualities. Access to historical data, critic scores and current prices can help an investor identify whether a wine represents a good opportunity. Things to look out for include brand prestige, price per point, investment appreciation over different time frames and drinking windows. One can also get help from experts who understand the intricacies of the market, utilize the latest technology and closely follow the trends.
Stability, sustainability and profitability
Today’s investors are looking for stability, sustainability and profitability. Different from last year, they are often less prepared to invest in edgy technologies for the future. Instead, many are looking for solid investment results – ideally, ones they can hold. Fine wines fit this demand well. Although it already features in 45% of HNW portfolios, with average allocations of 13%, fine wine looks set to become even more popular. Like a classic vintage Champagne, the market is ready to pop.
Thanks to its diversity and growing attention from experts, producers and enthusiasts, fine wine could be well-placed to meet investors’ changing priorities in the years to come.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.