- The 1855 Bordeaux Wine Classification continues to serve as a touchstone that has shaped not only Bordeaux but also global perceptions of what constitutes a ‘fine wine’.
- Wine-producing regions worldwide have developed their own unique classification frameworks, based on quality, price, and terroir.
- Wine classifications serve as guides to quality standards, geographical origins, and historical context.
Wine classifications play a vital role in the global wine industry. They help consumers, collectors, and investors navigate quality, geographical origin, and prestige in an increasingly complex market. From Bordeaux’s classified growths to Burgundy’s vineyard-based crus, these frameworks provide structure in a world where thousands of producers and regions compete for attention.
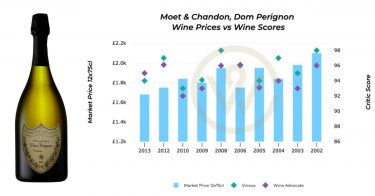
Among all wine classification systems, none has shaped perceptions of “fine wine” more profoundly than the 1855 Bordeaux Wine Classification. Commissioned under Napoleon III, this historic ranking established a hierarchy of growth wines that continues to influence how quality, rarity, and value are defined nearly 170 years later. While wine-producing regions across the world have since developed their own classification frameworks, the 1855 system remains a benchmark – both commercially and culturally – for what constitutes a truly great wine.
As the global wine market has evolved, classifications have adapted alongside it, offering insight into tradition, terroir, and shifting consumer preferences. Yet the enduring relevance of the 1855 Bordeaux Classification underscores the lasting power of reputation, consistency, and market trust in fine wine.
The enduring legacy of the 1855 Bordeaux Wine Classification
The Bordeaux Wine Official Classification of 1855 was commissioned for the Exposition Universelle de Paris, a world fair designed to showcase France’s greatest achievements. Napoleon III tasked the Bordeaux Chamber of Commerce with identifying the region’s finest wines. Rather than relying on tastings, the Chamber turned to wine brokers – the commercial gatekeepers of the time – who ranked estates based on historical reputation and long-established trading prices.
The classification focused primarily on prominent Left Bank estates, particularly in the Médoc, with one notable exception: Château Haut-Brion in Graves. These wines were divided into five hierarchical tiers:
-
Premier Cru (First Growth)
-
Deuxième Cru (Second Growth)
-
Troisième Cru (Third Growth)
-
Quatrième Cru (Fourth Growth)
-
Cinquième Cru (Fifth Growth)
Together, these tiers formed the foundation of Bordeaux’s system of classified growths, creating a permanent hierarchy that defined the region’s most prestigious growth wines.
The classification also recognised the exceptional sweet wines of Sauternes and Barsac, which enjoyed enormous international demand in the 19th century. At the pinnacle stood Château d’Yquem, placed alone in the rank of Premier Cru Supérieur — a distinction that remains unique in the wine world.
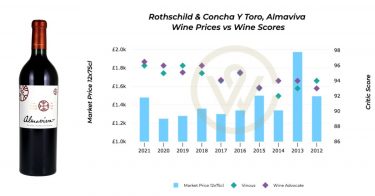
Remarkably, the classification has remained largely unchanged. Its most significant revision came in 1973, when Château Mouton Rothschild was promoted from Second Growth to First Growth. Baron Philippe de Rothschild famously marked the occasion with the words: “First I am, second I was, Mouton does not change.”
Criticism and evolution of a historic system
Despite its prestige, the 1855 Classification has long attracted criticism. Because it was based on 19th-century market prices, detractors argue that it fails to reflect modern viticulture, advances in winemaking, or evolving stylistic preferences. Over time, some non-classified estates have surpassed classified growths in quality, while benefiting from greater flexibility and innovation.
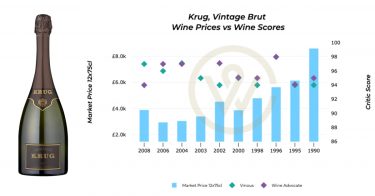
This rigidity has been both a strength and a weakness. On one hand, it has preserved clarity, brand power, and investment confidence. On the other, it has frozen a snapshot of historical market dynamics into a permanent hierarchy. In response to this tension, the global wine exchange, Liv-ex, has created a similar classification that uses price alone to determine a hierarchy of the leading fine wine labels in the market.
Nevertheless, the longevity of the 1855 system demonstrates the enduring value of reputation and consistency in the fine wine market.
How wines were ranked in the 1855 Bordeaux Classification
To understand why the 1855 Bordeaux Classification remains so influential today, it is essential to examine how the wines were ranked in the first place. Unlike many modern systems that rely on tasting panels or regulatory oversight, the 1855 framework was fundamentally commercial in nature.
A market-driven system
At the request of Napoleon III and the Bordeaux Chamber of Commerce, wine brokers ranked estates according to decades of trading data, merchant pricing, and auction records. Growth status was awarded based on sustained demand, reliability, and reputation rather than the performance of a single vintage.
The focus was firmly on red wines from the Left Bank, particularly the Médoc. These were organised into five growth tiers, creating a clear hierarchy of prestige. First Growth estates such as Château Margaux were already recognised in the 19th century for consistency and refinement, helping to cement their position at the top of the classification.
While red wines dominated, sweet white wines from Sauternes and Barsac were also included, reflecting their immense popularity at the time. The system culminated in the singular elevation of Château d’Yquem as Premier Cru Supérieur – a status unmatched by any other wine.
Notably, dry white Bordeaux was excluded altogether. At the time, these wines lacked the commercial prominence of red and sweet white wines, highlighting how closely the classification mirrored market realities rather than stylistic diversity.
Once established, growth status became fixed. Over time, this transformed a commercial ranking into a permanent hierarchy of classified growths, a structure that continues to shape demand for Bordeaux growth wines today.
The economic weight of the 1855 Classification
From an investment perspective, the 1855 Classification remains one of the most powerful brand frameworks in fine wine.
Today, the five First Growths – Château Lafite Rothschild, Château Latour, Château Margaux, Château Haut-Brion, and Château Mouton Rothschild – remain among the most recognised wines in the world. Their classified growth status directly correlates with market dominance:
-
They anchor indices such as the Liv-ex 50
-
They command sustained global demand, particularly in the US and Asia
-
Their brand prestige supports price resilience during economic downturns
-
Their growth wines are among the most actively traded worldwide
Beyond bottle prices, classification status also influences land values. Vineyards designated as crus classés command significantly higher prices than non-classified sites, shaping long-term investment, production strategy, and estate positioning across Bordeaux.
The Saint-Émilion Classification
Bordeaux’s Right Bank offers a completely different approach through the Saint-Émilion Classification, first introduced in 1955. Unlike the 1855 system, Saint-Émilion revises its rankings roughly every ten years, allowing producers to move up or down the hierarchy. Its tiers include:
The dynamism of this model fosters competition, encouraging châteaux to innovate, invest in vineyards, and elevate their winemaking standards.
However, the classification has experienced its share of controversy. The most notable recent development was the withdrawal of three top estates – Châteaux Ausone, Cheval Blanc and Angélus – from the classification amid disputes over evaluation criteria. This highlighted the tensions between heritage, modern wine styles, and market realities.
Despite these challenges, the Saint-Émilion system offers a compelling alternative to Bordeaux’s more rigid 1855 structure, showcasing a model that evolves with the industry.
Classifications beyond Bordeaux
Burgundy’s cru system: terroir above all
Burgundy takes a fundamentally different approach, classifying wines by vineyard site rather than producer. Its hierarchy includes:
-
Grand Cru
-
Premier Cru
-
Village
-
Regional
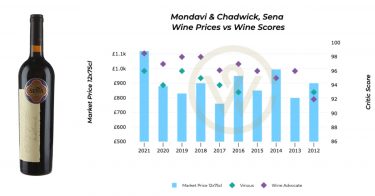
Because vineyards are often shared among multiple producers, two wines from the same site can vary significantly. This terroir-driven model has influenced regions worldwide, particularly in the New World, where vineyard identity increasingly defines top-tier wines.
Germany’s VDP Classification
Germany’s VDP system draws inspiration from Burgundy, with top vineyard designations such as Grosse Lage (Great Growth) and Erste Lage (First Growth). These categories identify sites capable of producing world-class wines, particularly Riesling, while allowing stylistic diversity.
Italy’s Barolo and Barbaresco crus
In Piedmont, Barolo and Barbaresco rely on an unofficial but widely recognised cru system. Vineyard names such as Cannubi, Brunate, and Rabajà carry prestige and influence pricing. The introduction of Menzione Geografica Aggiuntiva (MGA) in 2010 formalised many of these distinctions, strengthening the region’s terroir identity.
Portugal’s Douro Classification
The Douro Valley boasts one of the world’s earliest vineyard classification systems, dating back to 1756. Based on factors such as altitude, soil, and exposure, it predates Bordeaux by nearly a century and laid the groundwork for modern terroir-based classification models.
Concluding thoughts
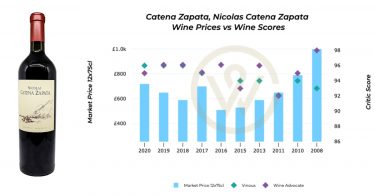
The 1855 Bordeaux Wine Classification remains one of the most influential frameworks in the history of fine wine. Its hierarchy of classified growths continues to shape global perceptions of quality, prestige, and value, particularly for investment-grade growth wines.
At the same time, more flexible models – from Saint-Émilion’s evolving rankings to Burgundy’s terroir-driven crus – demonstrate how classification systems can adapt to changing markets and consumer expectations. Together, these frameworks help define how wine is understood, traded, and collected worldwide.
From Europe to the New World, wine classifications act as both historical artefacts and modern benchmarks, guiding today’s collectors and investors through an ever-evolving fine wine landscape.
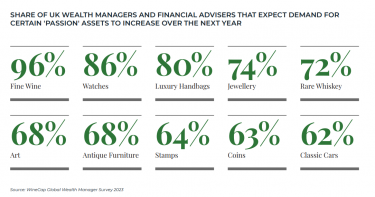
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.