- The 2022 vintage boasts high quality and quantity – ‘the largest crop in 23 years’.
- It is being launched in a downward market, following ten months of consistent price declines.
- As demand has tempered and stock has (re-)entered the market, the success of the upcoming releases will largely depend on pricing.
Burgundy’s 2022 vintage is being launched in a downward market, following ten months of consistent price declines. The success of the upcoming releases will largely depend on pricing, but will its quality and quantity have the potential to turn the tables?
Critical opinions on Burgundy 2022
Critic reports thus far have been overwhelmingly positive, applauding both the quality and the quantity of the vintage. 2022 marks the largest crop in 23 years, with some producers seeing double the yields of the previous year. According to Matthew Hayes (JancisRobinson.com), ‘across the whole of Burgundy, 2022 offered a whopping 75.4% more wine (red, white and crémant) compared with 2021’.
Contrary to expectations, the vintage produced wines with typicity, purity, and freshness despite the extreme weather. Hayes commented that ‘2022 was the second-hottest year that the Côte d’Or has endured this century and should logically have followed in the footsteps of the equally stifling solaire years of 2019 and 2020, producing wines with rich, deep fruit profiles and vibrant acidities to ensure long life but […] the wines show a generally impeccable balance of tidy, ripe fruit, discreet acidity and equally (and mostly) refined tannins’.
Hayes revealed that ‘the best-sited and best-rooted vines appeared to have coped well with the heat and in the Côte d’Or the excellence of the top premiers and grands crus shines clearly’.
The prevailing opinion is that 2022 is an excellent year for white wines, reminiscent of 2017 and 2020. Meanwhile, tasting notes from the Côte de Beaune and Côte de Nuits highlighted dense red wines with well-integrated tannins, simultaneously offering elegance and concentration. The wines are expected to be approachable in youth but with significant ageing potential.
However, the market onto which they are released is just as important as the releases themselves.
The current market for Burgundy
In October 2022, the Liv-ex Burgundy 150 index reached an unprecedented peak, marking a staggering 809.4% increase since its inception in December 2003. Twenty years later, Burgundy remains the best-performing fine wine region.
However, since its peak, prices have tumbled 17.4%. This decline has been attributed to various macroeconomic factors that led to a shift in investor sentiment. As the economic landscape became more uncertain, fine wine buyers have grown increasingly risk-averse, causing a contraction in demand for more volatile investments.
This trend was particularly pronounced in Burgundy, which had soared too high across the whole spectrum. At these stratospheric prices, the market saw more sellers than buyers, with investors keen to liquidate their stock. Top-tier Burgundy (re-)entered the market as sellers were looking to make gains.
This perception of increased risk and a preference for stability among investors led to a decrease in Burgundy’s trade share by value. The falling prices further exacerbated this trend.
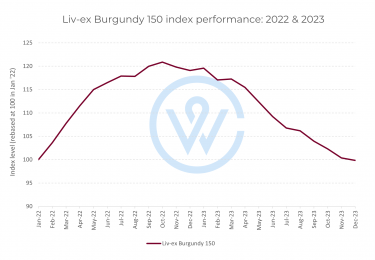
The market conditions present a challenging backdrop for the high-quality high-quantity Burgundy 2022 En Primeur campaign. Will the excitement of the new be enough to stimulate demand?
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.