- One of the key characteristics that make fine wine an attractive diversifier is its low correlation to traditional financial markets.
- Its scarcity and tangibility further drive up its value.
- According to the WineCap Wealth Report 2025, 96% of UK wealth managers expect demand for fine wine to increase, a testament to its growing recognition as a valuable asset class.
Moreover, fine wine’s value is tied to its provenance, condition, and aging potential, making it a tangible investment with intrinsic worth. Unlike cryptocurrencies or speculative stocks, which can experience extreme fluctuations based on sentiment or market cycles, fine wine benefits from an established secondary market where demand remains steady among collectors, investors, and luxury buyers.
Inflation hedge and wealth preservation
Fine wine serves as a natural hedge against inflation, protecting purchasing power when traditional assets are eroded by rising costs. As inflation increases, the prices of hard assets like fine art, real estate, and fine wine tend to appreciate, maintaining their value in real terms.
Wealth managers increasingly recommend allocating a small percentage of a portfolio to alternative assets like fine wine to safeguard against economic turbulence.
Tax efficiency for UK investors
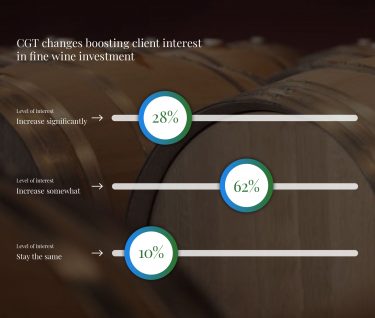
For UK-based investors, fine wine presents a significant tax advantage over traditional investments. Unlike stocks, real estate, or business assets that are subject to Capital Gains Tax (CGT), fine wine is classified as a “wasting asset”, meaning it has an anticipated lifespan of less than 50 years.
This classification makes fine wine exempt from CGT, allowing investors to realise profits without the same tax burdens as other asset classes.
For example, a traditional investment yielding a £5,000 profit could be subject to CGT at rates of up to 24%, reducing net returns. In contrast, a fine wine investment with the same £5,000 profit would be tax-free, maximising gains for high-net-worth investors.
This tax efficiency makes fine wine particularly attractive in wealth management strategies, especially as the UK government has lowered CGT allowances and increased tax rates in recent years.
Growing institutional and HNW investor demand
The perception of fine wine as a viable financial asset is rapidly evolving. Traditionally the domain of private collectors and enthusiasts, fine wine is now being incorporated into portfolios managed by wealth advisors, family offices, and institutional investors.
According to the WineCap Wealth Report 2025, 96% of UK wealth managers expect demand for fine wine to increase, a testament to its growing recognition as a valuable asset class.
Additionally, AI-powered investment tools are making fine wine more accessible to a broader range of investors. Fine wine companies and professionally managed portfolios allow investors to gain exposure without needing deep industry expertise.
This institutional adoption further legitimises fine wine as a serious financial instrument, enhancing its liquidity and long-term viability.
Why fine wine deserves a place in your portfolio
Incorporating fine wine into an investment portfolio provides stability, tax efficiency, inflation protection, and strong diversification benefits. Its low correlation with traditional assets makes it particularly valuable during periods of market uncertainty, while its scarcity-driven appreciation ensures long-term value retention.
For investors seeking to protect and grow wealth, fine wine remains one of the most compelling alternative investments available today.