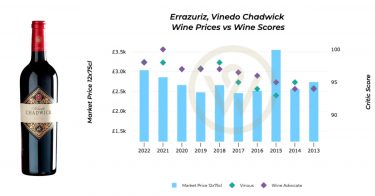
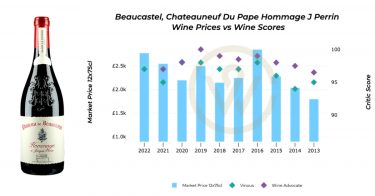
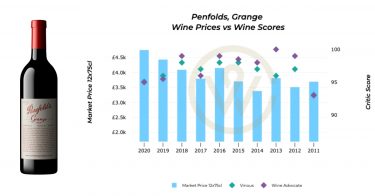
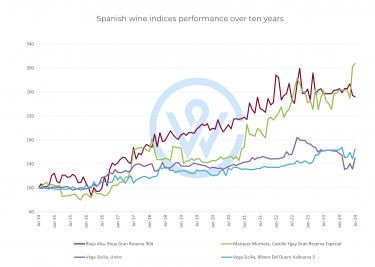
The nature of Bordeaux’s En Primeur campaign varies each year depending on growing conditions and market forces. However, one aspect is emerging as a strong trend across vintages: volumes released during En Primeur are decreasing.
WineCap spoke with prominent Bordeaux producers for deeper insights into the reasons for this pattern.
- Interviewed châteaux release between 60% and 90% En Primeur.
- Rising temperatures and organic farming reduce yields and En Primeur offerings.
- Châteaux need to consider both on- and off-trade customers.
- Climate change necessitates holding wine for style, and brand preservation in future.
- Competition to produce the highest quality reduces volume.
Decreased production and adaptable approach
Several producers WineCap interviewed explained that, in addition to the variable vintages typical of the Bordeaux region, global warming and changing vineyard practices are lowering yields.
Château Pichon Comtesse, Second Growth, Pauillac
Nicolas Glumineau, CEO and winemaker, recognised lower yields and wine volumes in recent years as contributing to the changing dynamics of the En Primeur system.
‘For Pichon Comtesse, it’s not due to the fact that we want to retain more volumes here in the cellars,’ Glumineau told WineCap. ‘I really do believe in the En Primeur system, despite seeing less and less volume of wine released this way. Volumes released have gone down because of lower yields over the last ten to 15 years. Still, I want to play the game of En Primeur, so that’s why we release something like 80% of our production every year’.
Château Smith Haut-Lafitte, Grand Cru Classé, Graves
Florence Cathiard, co-owner with her husband Daniel of Château Smith Haut-Lafitte, said that low yields influenced their decisions to reduce En Primeur volumes but commented that it was possible some maneuvering occurred.
‘For us, it’s not voluntary. It’s because of organic certification, which means we tend to have too low volumes,’ she said.
Château Margaux, First Growth, Haut-Médoc
‘The En Primeur volume, of course, is lower than ten or 20 years ago because the yield is much lower than before. Also, we are much more demanding in our selection for Château Margaux. So the total volume of Château Margaux has decreased tremendously,’ managing director, Philippe Bascaules, told WineCap. ‘That said, the quantity of En Primeur hasn’t changed a lot. Depending on the vintage, we can sell 70% to 85% of the production’.
Bascaules emphasised that it was the level of the yield and strict selection for quality control, rather than the house’s reluctance to participate, that created an impression of reduction. ‘En Primeur is very important for us’.
Château Pavie, Premier Grand Cru Classé (A), Saint-Émilion
‘At Château Pavie, we haven’t really changed the policy of let’s release less wine or let’s release more wine,’ Olivier Gailly, commercial director, said. ‘We adapt vintage to vintage. There is no strict rule as to what we want to release; the percentage might change vintage after vintage, depending on the dynamic of the market and of the vintage itself’.
Château Clinet, Pomerol
‘I think the main reason for the reduction in En Primeur volumes is the fact that sustainable viticultural practices reduce the volumes made per producer,’ Ronan Laborde, managing director and owner, explained.
‘Also, there is a strong competition to produce the best wine possible. You cannot do this with high volumes. So that’s why you also see more and more Bordeaux wine producers offering second wines or sometimes third wines. So, the quantity produced on the first wine is reduced. I think these are the two main reasons why the En Primeur volumes that are offered seem to be smaller than in the past’.
Customer choice
While some Bordeaux producers have a flexible strategy to their En Primeur releases, others believe that such versatility can have drawbacks, and that producer marketing and client demand should dictate stability in decision-making.
Troplong Mondot, Premier Grand Cru Classé B, Saint-Émilion
Ferréol du Fou, commercial director of Troplong Mondot, described lowering En Primeur quantities as ‘a huge mistake’, citing customer appetite as a key driver to the house’s stance.
‘Our strategy is to release 80% of the production every year, even if production is low. People need wines, and we need to show the label to the world. En Primeur is a way to offer a good deal for the consumer’.
Château Beau-Séjour Bécot, Premier Grand Cru Classé B, Saint-Émilion
Julien Barthe, who co-owns Château Beau-Séjour Bécot with his wife Juliet, has a similar position.
‘I think it’s a big mistake for many châteaux because they want to increase their prices, so they deliver a small volume. I really don’t think it’s a good way to promote your wine,’ he told WineCap. ‘This is not the case at Beau-Séjour Becot. We release around 85% to 90% of our production every year because we want to offer a good number of bottles to all our clients. We want to say ‘thanks, guys, you buy my wine, we are happy, we will be happy when you drink this wine’’.
Château Pichon-Longueville Baron, Second Growth, Pauillac
Christian Seely, managing director of AXA Millésimes, which owns Château Pichon-Longueville Baron, also believes that offering customers options is crucial, even if this involves holding a substantial amount of stock.
‘We release about half of our production of Grand Vin En Primeur, and we keep the other half back for a number of years,’ he said. ‘The reason we do that is that it gives our customers two options; if they want to buy En Primeur, they can. If they don’t feel like buying En Primeur and would like to come back and buy the wine from the property five years later, we still have stocks of wine for them here. The chances are it’s going to be a little bit more expensive a few years later, but it would have been kept in the perfect location at the property. So, by doing half En Primeur and half stock available at the château, we feel that we’re offering our customers the choice’.
Châteaux traditional commercial activities
An important influence on En Primeur release quantities for several chateaux is retaining volumes to maintain established business activities on site and throughout on- and off-trade networks.
Château Beychevelle, Fourth Growth, Saint-Julien
Philippe Blanc, general manager of Château Beychevelle, stressed to WineCap that the house took local customers into account when making decisions about what levels of wine to release En Primeur.
‘We don’t play the scarcity game, we play the game of En Primeur’, he said. ‘We’ve got over 100 negociant customers, which is a lot, and we sell 85% of our production En Primeur. Before 2016, we were selling 95% or 96%, which is extremely high. We were frustrated to not have any volumes of available wines for doing anything. For example, if tomorrow you decided you wanted to have an event with us, we could make an event because we always have enough wine for drinking, but we have no wine for selling. It was a bit frustrating for us and the merchants here or abroad when they asked for, say, five cases of wine for customers, and we had no wine. So, we decided to decrease the shares sold En Primeur to 85%.’
Blanc went on to explain that, while there had been a decrease in En Primeur volumes, there was no intention to go lower. ‘And why are we so dedicated to En Primeur? Beychevelle, as you probably know, is a wine which increases its value over time, and our golden rule is that the Primeur price is the lowest you can get. We could say, okay, keep more, because the price will go up, but we don’t want this policy, because setting the price at a more reasonable level makes it possible to sell it to the traditional market. So, we stick to that.’
Château Canon, Premier Grand Cru Classé, Saint-Émilion
Nicolas Audebert, winemaker and general manager of the Saint-Émilion estate, has the same perspective on En Primeur with the house operating within its framework. It also considers the on-trade environment when making decisions about wine proportions for the annual campaign.
‘We consider that the En Primeur moment and campaign are extremely important, and we play the game. We do not put a small volume in En Primeur,’ he told WineCap. ‘Of course, we keep some volume here at the chateau to be able to have wine for the next 20 years, to have wine for the bibliothèque, and be able to do fantastic tastings 80 or 100 years from now.’
The chateau puts a minimum of 70% of the production, every year, En Primeur, with Audebert describing it as a ‘fantastic time where everybody’s looking at Bordeaux’ and ‘a win-win for the consumer and for us’.
Château Cheval Blanc, Saint-Émilion
At between 60% and 70%, Pierre-Oliver Clouet, winemaker and the technical manager at the Right Bank house, sometimes commits even lower amounts than peers to the En Primeur campaign.
‘We keep around one-third of our crops to sell in five, ten, or 15 years, to have an opportunity to provide some bottles to restaurants, wine shops, or distributors who don’t have the opportunity to have storage. We alter the model a little between two-thirds En Primeur and one-third available for the market – ready-to-drink, in fact’.
Wine heritage
For Cos d’Estournel, the annual En Primeur allocation decision relates to the house’s legacy: mitigating the impact of climate change on the classic and recognisable style of the house’s wine is of prime concern.
Cos d’Estournel, Second Growth, Saint-Estèphe
‘Well, in terms of En Primeur, the volumes are quite different compared to before because before, the context was different,’ commercial director Charles Thomas told WineCap. ‘Twenty, 30, or 40 years ago, when you couldn’t sell your wine, you would sell all your wine if you could. Also, when you look at global warming, the style of wine could be a bit different in 20 years. So, in terms of style, it’s also quite important to keep some wine that we make now and to be able to release it later on.’
See also our Bordeaux I Regional Report.


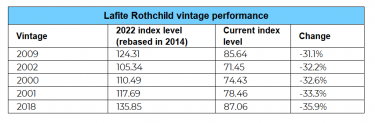
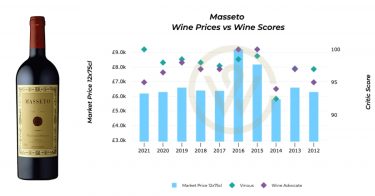
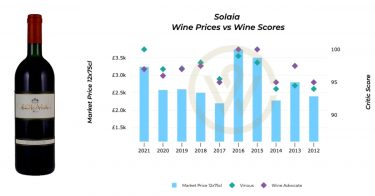
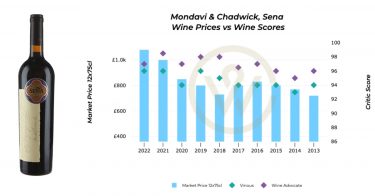
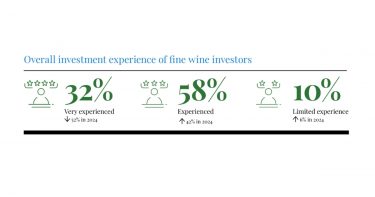 *UK
*UK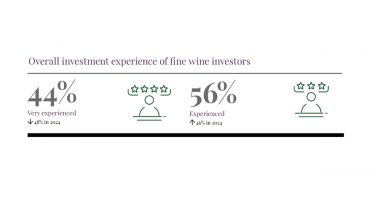 *US
*US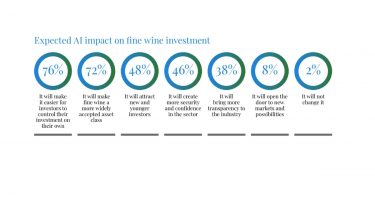 *UK
*UK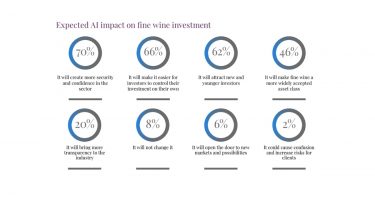 *US
*US