A version of this article by WineCap’s CEO Alexander Westgarth was first published in Forbes.
- Fine wine has been traded for millennia although its popularity as an investment is more recent.
- The fine wine market’s stability compared to stocks make it an effective volatility smoother, preserving wealth during market downturns.
- Investors should consider factors such as illiquidity risk, storage costs, and insurance coverage, while positioning wine as a complementary asset within a diversified portfolio.
The world of fine wine has long captivated investors with its timeless allure. Wine appreciation and collection is one of the oldest practices; the ancient Greeks, Egyptians, Phoenicians and Romans were all big traders of wine. Perhaps the first evidence of wine investment in the more traditional sense can be found in the writings of Thomas Jefferson, America’s third president. In 1787, he wrote that the 1786 vintage for top Bordeaux wines cost 1800 livres per tonneau compared to 2000 livres for the older 1783.
Today, the fine wine market is gaining popularity, not just among oenophiles; investors and wealth managers are looking to reap the benefits of this diverse asset class. New participants are eager to ensure they avoid potential pitfalls and make informed investment decisions. This article provides some of the key considerations for successful wine investing, showcasing the market’s potential at a glance.
Wine as a hedging asset
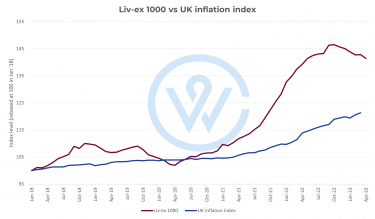
When constructing a well-rounded investment portfolio, it is crucial to consider the inclusion of fine wine as a hedging asset. Fine wine has a historical track record of retaining and increasing its value, even during periods of economic recession or financial uncertainty. Recent years are a case in point. While the world grappled with pandemics, wars and inflation, fine wine enjoyed an incline. Over the last half-decade, the average bottle of fine wine has increased in value by a notable 45%, according to the Liv-ex 1000 index.
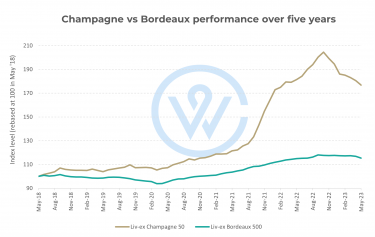
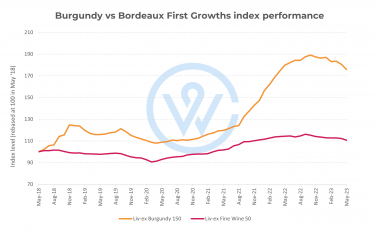
Certain wines did exceptionally well over the pandemic. The standout players were Burgundy, Champagne and Bordeaux. At the start, fine bottles of Burgundy were selling for just under £200 (May 2020). But within two and a half years, average prices soared to over £325 (September 2022)—a return of 62%.
There are several reasons why wine tends to buffer against market shocks. Firstly, as a physical asset, it is less sensitive to inflation – just like property, gold or excellent art. Secondly, the market is private. Buyers are often high net worth or ultra-high net worth individuals, so they are wealthy and passionate. Thirdly, it is a rare and depleting asset.
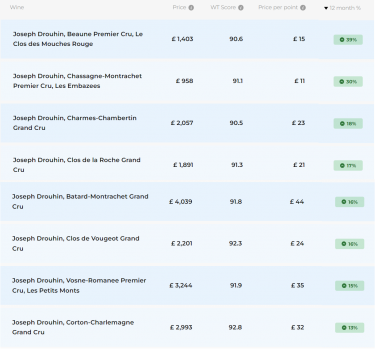
The scarcity factor of fine wine makes it increasingly valuable over time. As purveyors open bottles, the demand outweighs supply and prices can soar. For instance, Domaine Leroy’s Nuits-Saint-Georges’ Aux Lavieres has experienced a remarkable 353% increase in value over the past five years, driven by its scarcity.
Wine can smooth out volatility
An excellent wine must be enjoyed slowly. In the same way, the wine market tends to move at a more gentle pace too. While stocks can sky-rocket or plummet in weeks, wine movements often take months. This can add much-needed stability to investment portfolios.
Wealth managers have harnessed the volatility-smoothing properties of wine to offset the erratic performance of other assets. Even a modest allocation of up to 10% can significantly reduce overall portfolio volatility and act as a valuable tool during market downturns. When inflation rockets, it can also help to preserve some of the wealth eroded through bonds and cash-like instruments.
Liquidity, storage and insurance considerations
Potential investors should be mindful of the illiquidity risk associated with wine investments. While the wine itself is a liquid asset, the investment tends to lack immediate liquidity. Investors should carefully assess their liquidity needs before embarking on a wine investment journey. Those who might need quick access to cash may want to include some cash-like investments like T-Bills or Bank CDs in their portfolio.
A buy-and-hold strategy typically yields the best results in wine investment. Selling too early can result in missed opportunities for substantial profits, especially when considering the maturity of the vintage. While digital platforms offer relatively quicker selling options, physical auction routes may take longer but can still deliver favorable outcomes.
Investors must also factor in the costs associated with wine investments. Unlike investing in public markets, fine wine incurs additional expenses such as secure storage and temperature control. Investors may also consider insurance, particularly when transporting wines between locations. Although these costs are generally affordable, it is advisable to research storage options, seek reviews, and negotiate insurance coverage within annual fees.
In the United Kingdom, fine wine investments often benefit from exemptions from capital gains tax. This favorable tax treatment can offset storage costs multiple times over, further enhancing the investment’s attractiveness.
Investing soberly
While the potential for substantial returns in fine wine investment is evident, it is crucial to navigate the market with prudence and awareness of potential pitfalls. Investors should maintain sufficient liquidity in their portfolios to handle unforeseen emergencies and consider the long-term costs associated with wine investments.
The key to successful wine investing lies in positioning wine as a hedging asset and volatility smoother within a broader array of assets. Although an exceptional bottle of wine holds its own allure, it should not overshadow the rest of the portfolio. Wine should be viewed as a stable and valuable component, working harmoniously with other investments to help investors achieve their long-term financial goals.
With careful consideration of market dynamics, wine’s inherent hedging properties, and a prudent approach to investment, investors can embrace the timeless elegance of fine wine while capitalising on its investment potential.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.