- Sustainability in wine encompasses various processes such as environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and long-term financial viability.
- Sustainability appeals to a growing group of investors who want their money to do good while it grows.
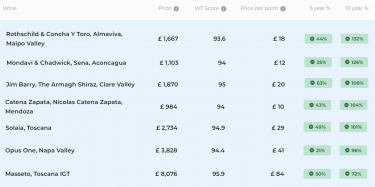
- Top wineries implementing sustainable practices include Bodega Catena Zapata and Château Pontet-Canet.
The wine investment market has diversified considerably in recent years, with sustainability becoming a core focus. As examined last week, environmental considerations are the number one reason why UK investors choose to invest in fine wine. Today’s article explores the criteria for sustainable wine, its appeal, risks and considerations, as well as the future prospects for this important market segment.
Defining sustainable wine
Sustainability in wine is a nuanced concept that goes beyond certifications like ‘organic’ or ‘biodynamic’ that you might find on a bottle’s label. These certifications are positive indicators but they do not provide a complete picture of a wine’s overall sustainability or its quality. In fact, while organic and biodynamic practices are steps in the right direction, they are not panaceas for all environmental challenges facing vineyards and wineries.
Truly sustainable wines are produced with a broader vision that encompasses not just environmental considerations, but also social and economic aspects. This holistic approach involves responsible land use, ethical labour practices, and a focus on long-term financial viability for producers.
Organic, biodynamic, and sustainable – what is the difference?
Organic wines are made from grapes grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilisers. Biodynamic wines take this a step further by integrating the vineyard into a self-sustaining ecosystem.
Sustainable wines, however, encompass a broader range of practices aimed at the long-term viability of the entire wine-producing operation. Various certifications, such as ‘Certified California Sustainable Winegrowing’, exist to label these wines officially. Organisations such as Sustainable Wine work to enhance clarity around sustainability in the industry as a whole from viticulture to packaging solutions and logistics.
The appeal of sustainable wines
Sustainability appeals to a growing cohort of investors who want their money to do good while it grows. Investing in sustainable wines satisfies this ethical imperative, thereby adding another layer of attraction to the investment.
Studies indicate a rising demand for sustainable products, including wine. This increased consumer demand means greater sales potential and, by extension, a probable rise in value for these wines over time.
Sustainable wines often come with compelling stories of environmental stewardship and community support. This narrative adds a unique selling proposition that can boost brand value and investment potential.
Risks and considerations
Like any investment, putting money into sustainable wines is not without risk. Market volatility, consumer preferences and supply and demand can impact returns as with any other investment-grade wine.
Another risk lies in the potential for ‘greenwashing’, where a wine’s eco-friendly credentials can be exaggerated. Investors must perform due diligence to ensure they are backing genuinely sustainable ventures.
How to invest in sustainable wines
The first step is comprehensive research: utilising online resources, expert reviews, and consumer reports to assess a wine’s investment potential and sustainable credentials. Diversifying your portfolio by including a mix of sustainable wines from various regions and price points can mitigate risks and increase the potential for rewards.
Pay close attention to ratings from renowned wine critics and industry experts. A high rating can significantly impact a wine’s market value.
Sustainability pioneers
Several wineries around the world are setting the bar high for sustainable practices. Frog’s Leap in Napa Valley is known for its organic and dry farming techniques. Germany’s Weingut Wittmann has also embraced organic farming and natural winemaking processes. In Argentina, Bodega Catena Zapata stands out for its sustainable farming and research into high-altitude winemaking. Château Pontet-Canet in Bordeaux is another success story, having converted to biodynamics in 2014 after various setbacks in 2007. Their journey underscores the long-term dedication needed for truly sustainable winemaking.
Future outlook
From water-saving technologies to renewable energy, the wine industry is continually adopting more sustainable practices, pointing to a robust market future. Experts predict the demand for sustainable wines will only grow, particularly as younger generations who prioritise sustainability come of age.
Sustainable wines present a captivating new frontier in wine investment, promising both ethical satisfaction and financial gains. As with any investment, there are risks, but the burgeoning market for these wines, coupled with their unique branding advantages, makes them a trend worth watching. For investors willing to do their homework, the opportunity is ripe for the picking.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.