- The impending largest intergenerational wealth handover is driving the expansion of the collectibles market.
- Demand is rising among younger investors looking to diversify their portfolios with assets that offer uncorrelated market returns.
- Fine wine is the most popular collectible among UK investors, followed by luxury handbags and jewellery.
From luxury handbags to fine wine and whisky, the collectibles market is expanding and attracting rising demand from investors that is set to continue.
This shift is driven by the onset of the largest intergenerational wealth handover in history and a growing appetite among younger investors to diversify their portfolios with assets that offer uncorrelated market returns.
The evolution of the collectibles market
The allure of collectibles as investments is not a recent phenomenon. Historically, items like fine art, rare coins, and vintage wines have been appreciated for their aesthetic and cultural value. During periods of economic uncertainty, tangible assets like these often retained their value better than traditional financial instruments. For example, during the Great Depression, art and rare coins rose in price, providing a hedge against financial market volatility.
In the post-World War II era, the collectibles market began to gain more structure and legitimacy. Auction houses such as Sotheby’s and Christie’s played pivotal roles in establishing benchmarks for the value of fine art and antiques. The rise of specialised indices, such as the Mei Moses Art Index, helped quantify returns on art investments, further opening the market.
The collectibles market has further evolved in recent years with the help of technology. Technological advancements have democratised access to market information and trading platforms, making it easier for investors to track market trends and make informed decisions. Indices like Wine Track help prospective investors see the average price of a wine, critic scores and investment returns over different time periods for free and at a glance.
A testament to the rising demand is the expansion of the market. According to investment bank Nomura, the art and collectibles category is now larger than private assets ($1.6 trillion) and more than twice the size of private debt markets ($0.8 trillion).
The most wanted collectibles for portfolio diversification
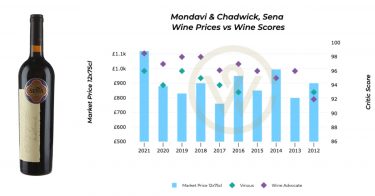
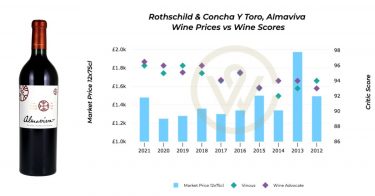
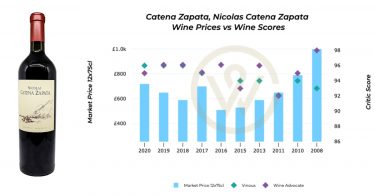
Among collectibles, fine wine is king. 92% of UK wealth managers anticipate demand to increase in the next year. Compared to other luxury assets, the fine wine market is more established and less volatile, offering increased liquidity and price transparency.
The second most popular collectible in 2024 is luxury handbags, with 86% of wealth managers expecting demand to rise further. As recently explored, interest in handbags as an investment has grown in line with rising prices in the primary market. For instance, the price of the Chanel medium classic flap bag is up close to 553% since 2005, and 4,809% since 1955.
Jewellery is the third most popular collectible in 2024 for 84% of wealth managers, followed by coins (82%). The fifth spot is shared by watches and rare whisky at 78%.
When it comes to the latter, fine wine investment companies are already capitalising on this trend by branching out into spirits. While its secondary market is still in the early stages of its development, rare whisky has already set pricing records.
Earlier this year, a 30-year-old bottle of The Emerald Isle by The Craft Irish Whiskey Co. sold for a staggering $2.8 million, breaking the world record for the most expensive bottle ever sold. The previous record was held by a 1926 Macallan bottle priced at $2.7 million. These figures dwarf the record for the most expensive fine wine ever auctioned, the 1995 Domaine de la Romanée-Conti Grand Cru, which fetched $558,000.
Collectibles vs mainstream investments
The rise in demand for collectibles comes at a time when traditional investments, like stocks and bonds, are facing heightened volatility and lower returns. Collectibles offer a unique proposition: they are not directly correlated with financial markets, providing a hedge against market downturns.
Moreover, collectibles have an intrinsic value tied to their rarity, cultural significance, and aesthetic appeal, which can appreciate over time independently of market conditions.
The stability and growth potential of these assets make them attractive alternatives to traditional investment avenues, and investors are increasingly perceptive of these benefits.
As the market for collectibles continues to evolve, clients are likely to find new and exciting opportunities in this dynamic sector.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.