- Wine ratings play a crucial role in wine investment, with high scores from influential critics impacting demand and market value.
- To use ratings effectively, investors should consider both the initial score and potential for growth.
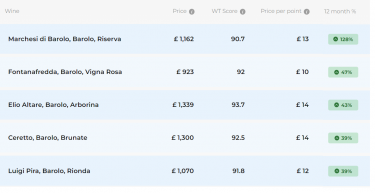
- The Wine Track score provides a broader view of a wine’s quality across multiple vintages and publications, helping investors assess wines at a glance.
In the fine wine market, few factors influence demand and long-term value as powerfully as wine ratings. For collectors and investors building an investment grade wine portfolio, scores from leading critics act as signals – not only of quality, but of longevity, market confidence, and future price potential.
However, while high scores often attract immediate attention, successful wine investment requires a deeper understanding of how ratings work, how they evolve over time, and how they interact with broader market forces such as global demand, scarcity, and drinking windows.
This article explores how wine ratings shape the fine wine market, how investors use them strategically, and why aggregated tools such as the Wine Track Score provide a clearer framework for assessing investment grade wines over the long term.
Why wine ratings matter for investment grade wine
Wine ratings emerged as a way to communicate quality quickly in an increasingly complex global wine industry. Today, they play a central role in shaping demand, pricing, and investor behaviour.
For wine investors, ratings provide insight into:
-
Quality and consistency across vintages
-
Longevity, including projected drinking windows
-
Market demand from collectors and consumers
-
Price stability in the secondary market
-
Investment potential relative to comparable wines
High scores from influential critics such as Robert Parker, Neal Martin, Jancis Robinson, James Suckling, and publications like Wine Spectator can materially affect prices – sometimes within days of publication.
As a result, ratings have become foundational to identifying investment grade wine, particularly for those seeking long-term capital appreciation rather than short-term trading.
How wine ratings influence the fine wine market
The fine wine market operates on reputation, scarcity, and trust. Ratings reinforce all three.
1. Ratings can drive immediate price movements
When a wine receives a benchmark score – especially 99+ or 100 points – it often enters a new tier of desirability.
A clear example is Marqués de Murrieta Castillo Ygay Gran Reserva Especial 2010, which saw rapid secondary-market price appreciation after being named Wine Spectator’s Wine of the Year. Similar reactions have historically followed 100-point scores awarded to Bordeaux First Growths and Burgundy Grand Crus.
For investment grade wine, wine scores act as a catalyst, accelerating demand and compressing supply.
2. Ratings shape long-term reputation
Consistent scoring matters more than isolated highs.
Producers such as:
have built long-term investment credibility through repeated critical recognition. This consistency supports price resilience, even during broader market corrections.
For wine investors, this track record is a key differentiator between speculative wines and true investment grade wine.
3. Ratings influence regional prestige and global demand
Critics can also elevate entire regions, beyond just individual wines.
-
Robert Parker’s support helped propel Napa Valley into the global investment spotlight
-
James Suckling championed Super Tuscan wines, accelerating international demand
-
Jancis Robinson played a key role in highlighting Austria’s quality renaissance
As regional reputations rise, so does global demand – a crucial driver of long-term price appreciation in investment grade wine.
Ratings change over time – And so do investment opportunities
One of the most misunderstood aspects of wine ratings is that they are not fixed.
As wine matures in bottle, critics often revisit their assessments. Tannins soften, structure integrates, and complexity develops – sometimes leading to upward score revisions.
The impact of score changes
-
Upward revisions often trigger renewed buying interest
-
Downward revisions may stall demand or price momentum
-
Barrel scores can differ meaningfully from bottled assessments
This evolution creates opportunity for informed investors.
Strategic approaches for investors
-
Buy early when barrel scores and critic commentary are strong
-
Hold strategically as wines approach peak maturity
-
Sell your wine when demand aligns with optimal drinking windows
Understanding how ratings interact with a wine’s maturity curve allows investors to identify undervalued vintages before wider market recognition.
Knowing the critics and their influence on investment grade wine
Not all critics evaluate wine the same way.
Robert Parker, for example, historically favoured powerful, concentrated styles from Bordeaux, California, and the Rhône. As his influence has waned, the critical landscape has diversified, reflecting broader consumer preferences for balance, freshness, and terroir expression.
For wine investors, understanding critic bias is essential. A wine overlooked by one reviewer may be favoured by another, particularly in more divisive regions like Burgundy, Piedmont, or Germany.
This diversity reinforces the importance of looking beyond single scores when assessing investment grade wine.
The Wine Track score – ratings at a glance
To address inconsistency across critics, many investors now rely on aggregated metrics.
The Wine Track Score provides:
-
A unified 100-point score
-
Data from 100+ critics across 12 major publications
-
Vintage-by-vintage performance tracking
-
Insight into producer consistency over time
By smoothing out individual preferences, the Wine Track score offers a more holistic view of investment grade wine performance – particularly useful when comparing regions, estates, or vintages.
Using ratings strategically in a wine investment portfolio
Ratings are most effective when used as part of a broader framework.
1. Identify consistently high-scoring producers
Bordeaux First Growths, Burgundy Grand Crus, and top Napa Cabernet producers continue to anchor the fine wine market because of sustained critical support.
2. Look for sleeper vintages
Some wines receive modest early scores but improve significantly with age. These vintages often offer strong risk-adjusted returns.
3. Understand vintage variation
Even elite producers experience variability. Ratings help identify which vintages offer superior long-term value.
4. Use aggregated data
Relying on multiple critics reduces bias and improves decision-making.
5. Align with drinking windows
Wines approaching peak maturity often see increased demand from drinkers, supporting secondary-market pricing.
Ratings are powerful but not the whole story
While ratings are essential, they are only one part of evaluating investment grade wine.
Investors should also consider:
-
Producer reputation
-
Vineyard classification (e.g. Grand Cru, First Growth)
-
Market liquidity
-
Provenance and storage facility conditions
-
Historical price performance
-
Long-term global demand
Professional storage in bonded warehouses preserves quality and protects value – a critical factor when preparing to sell wine in the future.
Building a long-term investment grade wine portfolio
In today’s fine wine market, ratings remain one of the most influential tools available to investors. They help signal quality, predict demand, and highlight wines with the potential to outperform over time.
However, ratings are most effective when paired with market insight, disciplined storage, and a long-term perspective. When used intelligently, they can help investors build resilient portfolios anchored by true investment grade wine.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.