- Global critic lists show unprecedented diversity across regions and styles.
- Bordeaux 2022 was in the spotlight across major publications.
- Collectible wines and investment-grade wines differ – only some critic favourites have long-term market potential.
Each November, major critic publications around the world release their annual Top 100 wines of the year rankings. Rather than showcasing the wines only released in the past twelve months, the lists highlight standout bottles tasted throughout the year, spanning vintages, regions, and stylistic expressions.
A clear trend emerges from looking at past and current lists: increasing diversity. Critics are no longer focusing exclusively on tried-and-true regions like Bordeaux, Napa, or Barolo. Instead, their selections – this year spanning wines from Etna to Stellenbosch, Central Otago to Morgon – reflect the global expansion of fine wine quality, elevated vineyard management, and the growing maturity of the market.
Critic choices largely align with broader shifts seen in the fine wine investment landscape. As quality rises around the world, more wines now boast age-worthiness, critical acclaim, and technical precision. However, this raises an important point: not all critic-favourite wines carry investment potential.
A collectible wine may be rare, high-scoring, or culturally important, while an investment-grade wine must also demonstrate a proven secondary-market track record, liquidity, stable long-term demand, and price performance history.
Below, we explore three of the most influential 2025 global rankings and what the top wines reveal about the state of the fine wine market going into 2026.
Wine Spectator’s Wine of the Year
Wine Spectator’s annual Top 100 list is arguably the most commercially impactful ranking in the global wine calendar. Historically, the No. 1 Wine of the Year has triggered immediate surges in demand, and often dramatic price rises, across global markets. A clear example came in 2023, when Argiano Brunello di Montalcino 2018 – previously quiet on the secondary market – experienced a rapid uptick in both demand and value within days of receiving the top spot.
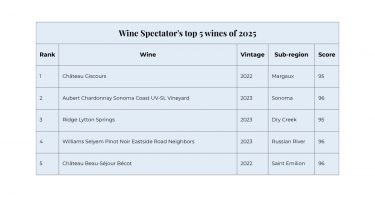
In 2025, the top position went to Château Giscours 2022, marking a major endorsement for Bordeaux’s strong 2022 vintage at a time when the region often finds itself facing criticism. Senior Editor James Molesworth explains: ‘Recent vintages have been mercurial in quality, while the region’s annual spring en primeur campaigns have fizzled. Tariffs haven’t helped. But if you needed a reminder that Bordeaux still makes some of the greatest wines in the world – and that its producers can evolve with changing times – the Château Giscours Margaux 2022 is your wine. This third-growth classified estate earns our top honor this year.’
Molesworth further highlights the wine as the culmination of decades of rebuilding work at the estate: ‘The efforts of Van Beek to surpass numerous obstacles over a generation is a clear example of how wine is a long game.’ The critic notes that recent improvements, including refined harvesting practices and guidance from consultant Thomas Duclos, have helped elevate quality, vintage after vintage. In 2022, these efforts culminated in a grand vin that Wine Spectator describes as fresh, seductive and finely detailed, with no second wine produced due to the exceptional quality of the harvest.
The rest of the top four represent a strong showing for California. Aubert’s UV-SL Chardonnay (No. 2) was praised as the union of ‘a renowned winemaker, a special vineyard and an exceptional vintage.’ Meanwhile, Ridge’s Lytton Springs 2023 and Williams Selyem’s Eastside Road Neighbors Pinot Noir 2023 reflect the continued strength and stylistic diversity of Californian wine across Dry Creek Valley and Russian River Valley.
Rounding out the top five is another Bordeaux 2022 wine: Château Beau-Séjour Bécot. Wine Spectator calls it a ‘dreamy wine’, reinforcing the broader pattern seen across both critic and market attention this year. Bordeaux 2022 is clearly one of the defining narratives of the 2025 rankings, earning major positions across multiple publications.
Vinous’ top 100 wines of 2025
Vinous’ annual list, which Antonio Galloni says aims to capture the ‘diversity and dynamism of today’s wine world,’ showcases wines of exceptional quality, character, and excitement rather than simply the highest-scoring bottles.
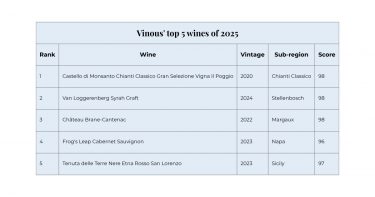
This year, Italy takes the top spot with Monsanto’s Il Poggio, which Galloni calls “a total stunner” and “one of the very finest Il Poggios ever made.”
One of the most notable placements comes at No. 2: Van Loggerenberg’s “Graft” Syrah 2024 from South Africa. Neal Martin awarded it 98 points, praising its mineral character, balance, and crystalline finish – another sign of South Africa’s accelerating rise in fine wine quality.
The third wine in the list represents a more classical pick, but with a symbolic shift. With ownership passing to Henri Lurton’s children, Martin sees the 2022 Château Brane-Cantenac as a defining benchmark: ‘A year when… the 2022 is a benchmark for the Margaux estate, its future North Star.’
The list continues with strong representation from both New and Old World producers, including Frog’s Leap’s classically styled 2023 Cabernet Sauvignon and Tenuta delle Terre Nere’s deeply structured Etna Rosso San Lorenzo.
James Suckling’s favourite wines of 2025
James Suckling’s team tasted over 45,000 wines in the last year, making his Top 100 one of the most globally comprehensive. His selections prioritise balance and drinkability – wines that shine immediately, whether from bottle or barrel.
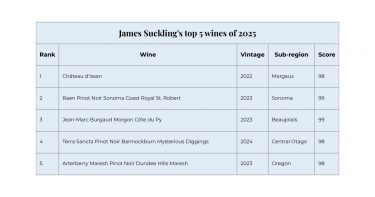
His top wine – Château d’Issan 2022 – reflects the broader dominance of Bordeaux’s 2022s across his list. Suckling emphasises that the vintage remains one of the biggest stories of the year, praising how the wines show focus, brightness and precision despite extreme heat and drought. He compares 2022 to other hot-vintage classics such as 1982, 1959, 1947 and 1928, all of which have stood the test of time, an important indicator for long-term growth.
Suckling also notes how the accessibility of 2022 Bordeaux – widely released, easy to sample, and available across markets – enabled more comprehensive evaluation this year, contributing to their strong representation.
The remaining wines illustrate the global reach of modern fine wine quality. American Pinot Noir features prominently, with standout bottles from Raen and Arterberry Maresh. Meanwhile, two of the most surprising inclusions – Burgaud’s Morgon Côte du Py and Terra Sancta’s Bannockburn Pinot Noir – are also among the most affordable on the list, reinforcing Suckling’s point about the exceptional value emerging from Beaujolais and regions such as Central Otago. His report proposes that once-overlooked regions are now producing wines of extraordinary finesse and consistency.
Across all three critic rankings, a consistent narrative emerges: fine wine quality is more global, diverse and dynamic than ever before. At the same time, the spotlight on Bordeaux 2022 signals a vintage with both critical momentum and long-term relevance, firmly positioning it as one of the defining investment stories of the year.
Not every critically acclaimed wine is an investment wine, but the themes that surface – regional momentum, stylistic shifts, the performance of key vintages, and the critics’ influence on market behaviour – will all shape the fine wine landscape as we move into 2026.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.