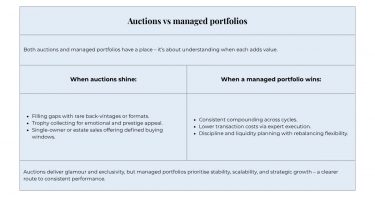
- Both auctions and portfolio approaches have a role to play in wine investment, but the latter is a more viable route to steady growth.
- Auctions can provide useful signals, but investors should identify and avoid market noise and hype.
- An expertly-managed portfolio focuses on growth, diversification, and liquidity over chasing auction trophy wines.
The wine world frequently makes headlines for astronomical prices at attention-catching auctions. Bottles can fetch sky-high sums as multimillion-dollar collections capture international interest. For investors, such record-breaking spectacles can appear to be proof of fine wine’s irresistible upwards trajectory.
However, glamorous and inspiring as they are, these auctions are not the market. They are the sharpest tip of it – distinct moments where scarcity, storytelling, and sentiment come together. A pristine bottle of Domaine de la Romanée-Conti or Château Pétrus with impeccable provenance might clear 20–50% above its estimate in a single-owner sale. While impressive, such outliers don’t speak of underlying market performance.
Understanding the difference between prices that make the news and the reality of the market is essential for any serious wine investor.
What ‘auction price’ really is
An auction price is more than meets the eye; it’s a composite shaped by multiple components. What does that sales figure really mean?
Hammer vs all-in costs
The hammer price is the winning bid declared by the auctioneer – but that’s not the final price. The buyer then pays a buyer’s premium (10%–25%), plus taxes, shipping, and insurance. A bottle that hits the headlines at £100,000 could ultimately cost the buyer £120,000.
Single-owner vs mixed-owner sales
Provenance is all-important. Bottles from single-owner collections, especially with engaging stories and original documentation, often command premiums far above market average. In contrast, mixed-owner sales tend to be a more accurate mirror of demand.
Estimate bands and marketing psychology
Auction houses set low and high estimates to guide bidding – and to generate excitement. These figures act equally as marketing tools and predictive indicators. Only a lot that exceeds the high parameter of its estimate band hits the news; one that sells within its estimated range represents the quieter reality.
True liquidity
A record price for a single bottle does not automatically translate into similar highs for other lots. Headline-making hammer prices are outliers, influenced by rarity, media coverage, and competitive auction frenzy rather than a broader trend in the market.
Wine auction record setters
The following are examples of headline-making auctions which illustrate the factors that drive remarkable performance: wine rarity, media frenzy, storytelling, and collector pedigree.
$34.5 mln – Henri Jayer, “The Heritage” (2018, Geneva)
- Legendary producer’s last 855 bottles from private cellar.
- 209 coveted magnums.
- Rare Vosne-Romanée vintages.
$28.8 mln – William I. Koch, “The Great American Wine Collector” (2025, New York)
- 750 large formats (Jeroboams, Methuselahs, Salmanazars).
- Leading Bordeaux, Burgundy, Rhône, Napa, and Piedmont wines.
- Single-owner collection.
$25.3 mln – Joseph Lau, “Iconic Wines” I–III (2022–2025, Hong Kong)
- Rare Burgundy and Bordeaux.
- Single-owner collection auctioned over three years created story.
$16.8 mln – Pierre Chen, “The Epicurean’s Atlas” (2023–2025, Hong Kong, Paris, Burgundy, New York)
- Iconic Burgundy, Bordeaux, Champagne, and New World wines.
- Legendary vintages.
$11.16 mln – Jacqueline Piatigorsky (2025, New York)
- Rare Lafite Rothschild vintages (1869–1941).
- Long-lost Château Lafite Vin Blanc.
- Media interest around collector pedigree.
These auctions were hugely successful, but outcomes weren’t solely due to wine calibre. The unique auction environment also played a role. Such heady sums are not necessarily representative of wider market pricing.
What auctions can tell investors
While not presenting a definitive picture, auctions do generate a treasure trove of information. However, it’s important to follow results with a discerning eye because not all of the information is useful for a wine investor. You need to learn how to separate signal from media noise to understand the true meaning of auction prices.
Useful signals for investors
- Provenance premiums: Illustrates how much collectors are willing to pay for documented bottles over generic lots. Formats, condition, and original packaging often contribute to worthwhile premiums.
- Bidding depth: The number of bidders within the estimate band indicates genuine demand. Likewise, consistent competition across lots can point to authentic appetite that exists beyond the auction house.
- Regional and vintage momentum: Repeated strong results across particular regions or vintages can signal emerging segments rather than one-off auction-driven prices.
- Thin trading: The highest-profile bottles typically sell only once a decade. Such rare transactions can provide valuable insights into the wider market.
Limits and noise
- Selection bias: “Survivorship bias” can distort average values. For a range of reasons, some wines survive the test of time while others don’t. Not every mature wine deserves high valuation.
- Seasonality and venue effects: Marquee sales held in the spring and summer tend to attract more bidders and media coverage, inflating prices temporarily. The location of the auction can also impact results.
- Story premium: Worth repeating is the character of the narrative surrounding an auction can elevate prices far beyond what would be achievable in normal market conditions. Celebrity collections, charity sales, and unique stories fall into this category.
Buying at auction
Auctions offer both opportunity and challenge for collectors and investors. Understanding their structure sets realistic expectations before bidding.
Pros
- Access to rare, mature stock unavailable at retail.
- Potential mispriced lots that savvy buyers can spot.
- Transparent, competitive pricing that benchmarks demand.
Cons
- Significant fees once premiums, taxes, and shipping are added.
- Condition risk from storage or cork issues.
- Time-intensive due diligence pre-auction.
- Limited resale liquidity; auction prices can be volatile.
Building a wine investment portfolio with a trusted manager
While auctions can offer wine performance insights, a structured, portfolio-driven approach is most optimal for serious investors. This method focuses on growth, diversification, and liquidity planning in response to the genuine market, rather than chasing one-off, high-performer auction house bottles. In short, headline bottles make news; diversified cases make portfolios.
Strategy-led
Discipline drives serious wine investment. A considered portfolio allocates across regions, producers, and vintages. Tiered maturity and style diversification help smooth returns and reduce volatility.
Execution
Acquiring wine at scale requires access to multiple channels: primary releases, négociant networks, ex-château allocations, and selective secondary market opportunities. Professional execution ensures consistent quality, provenance verification, and optimal pricing.
Expert oversight
A trusted manager maximises successful outcomes by safeguarding custody, insurance, and exit strategies, targeting holding periods and rebalancing, to shield investments from market swings.
Research & data
Continuous market monitoring is critical to disciplined investment. This data-driven strategy identifies trends and fair-value bands, so investors can avoid the pitfall of overpaying for hype and market noise.
Cost clarity
Unlike auctions, wine investment portfolio costs – custody, insurance, execution – are transparent upfront, allowing granular knowledge of charges for clear return comparisons.
Next steps
The fine wine world will always carry glamour, but serious investors should see auction headlines as stories, not signals. The real market for fine wine investment and value growth is built on data, liquidity, and expert execution rather than the excitement of ‘show-stopping’ headlines.
Key takeaways:
- Don’t fixate on record breakers – they rarely mirror market performance.
- Focus on repeatability and liquidity for sustainable returns.
- Calculate all-in costs for true value comparison.
- Diversify and plan exits through portfolio management for resilience.
Fine wine investment is guided by expertise, patience, data, and structure, separating steady compounding from the volatile environment of speculation.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.




 *UK
*UK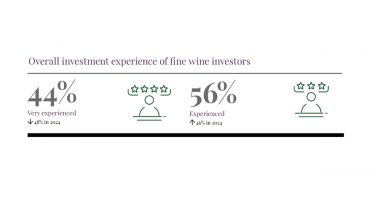 *US
*US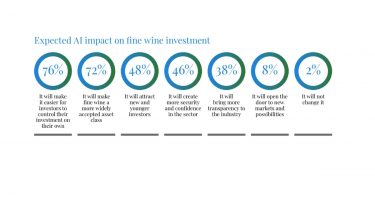 *UK
*UK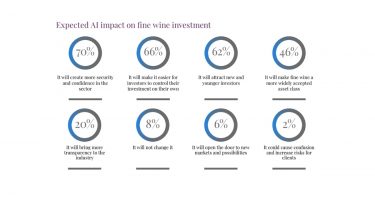 *US
*US