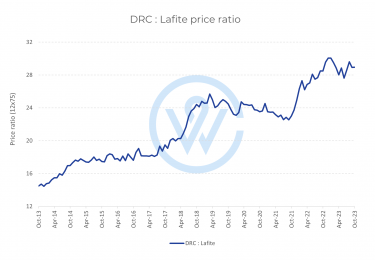
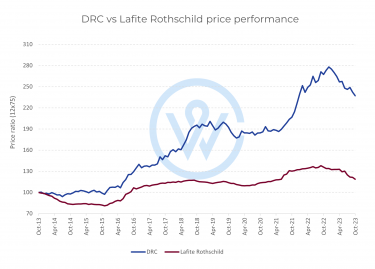
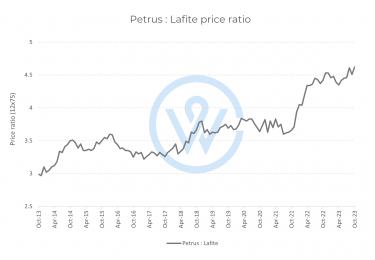
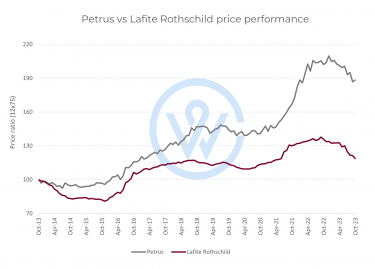
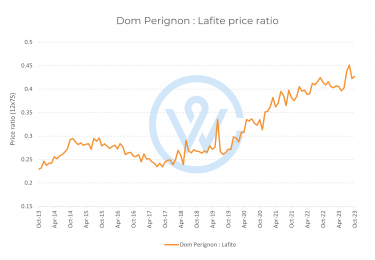
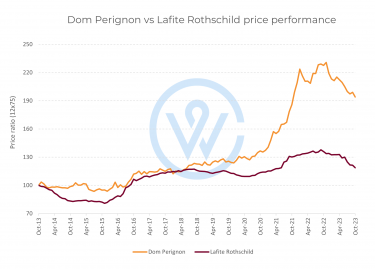
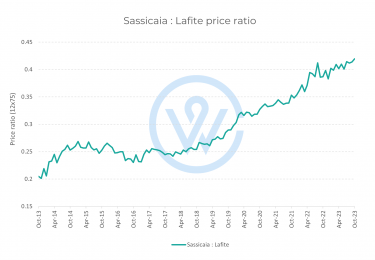
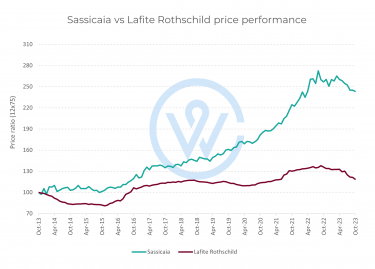
- The most important factors that affect fine wine prices are production costs, climate change, market demand, and economic conditions.
- Market demand is influenced by critic scores, rarity, producer reputation, vintage quality, and geopolitics.
- Understanding the factors that affect fine wine prices is key to making smart investment decisions.
Fine wine is more than just a luxury product – it is an asset class, a status symbol, and for many, a serious investment. While buyers might be aware of the rising value of sought-after labels, understanding the factors that drive these prices (upwards or downwards) is key to navigating the fine wine market.
In this article, we explore the primary factors affecting fine wine prices, including production costs, climate change, market demand, and broader economic conditions.
How production costs shape fine wine prices
At the heart of fine wine pricing are the production costs. The making of a high-end wine is a meticulous, labour-intensive process that is inevitably reflected in the price. So are the land costs, which can reach astronomic heights in famous fine wine regions like Burgundy, Napa or Bordeaux.
For instance, the luxury conglomerate LVMH recently acquired 1.3 hectares of Grand Cru vineyards on the Côte d’Or for 15.5 million euros. The purchase includes half a hectare each in Corton-Charlemagne and Romanée-Saint-Vivant, as well as 0.3 hectares in Corton Bressandes.
Besides land costs, manual labour and vineyard management can further affect release prices. The more human intervention required – whether in the vineyard or the winemaking process – the more costs add up.
Finally, many fine wines are not ready for release for several years after production. Extended ageing means producers incur additional costs, which in turn drives up prices for wines that are stored for longer periods before hitting the market.
The impact of climate change on fine wine pricing
In many traditional wine regions, unpredictable weather patterns, such as frost, heatwaves, and hailstorms, have resulted in lower grape yields. For example, the devastating frost in Burgundy in 2021 significantly reduced production, leading to a scarcity of wines from that vintage.
When yields are lower, the limited supply pushes prices higher, especially for in-demand producers. This scarcity effect can be seen in top wines like Domaine Leflaive or Domaine de la Romanée-Conti, where a challenging growing season can result in soaring prices.
Additionally, climate change is affecting the style of wines being produced. While some regions like Bordeaux are adapting to these new conditions, climate volatility has added another layer of unpredictability to wine prices. It has also facilitated the emergence of new wine regions, leading to a more competitive landscape.
Market demand and the rise of fine wine investment
Market demand is perhaps the most significant factor affecting fine wine prices. The most sought-after bottles usually rise in value, as quality improves over time and supply diminishes.
Producer reputation, vintage quality and scores from major critics like Robert Parker and Neal Martin play a key role here, informing buying decisions and pricing strategies. A 100-point wine often commands a significant premium to a 99-point wine. When it comes to the Bordeaux First Growths, for instance, the average difference between a 99-point and a 100-point wine is over £350 per case.
Market demand is also shaped by geopolitical factors. The global nature of wine trading platforms means that market sentiment can affect wine prices faster than ever before. Demand from China largely contributed to Bordeaux’s pricing surge in 2011, and today interest is moving towards Burgundy and Champagne.
Economic forces that influence fine wine prices
While the fine wine market generally operates with its own dynamics, macroeconomic factors such as inflation, currency fluctuations, and recessions can all have an impact.
In times of economic downturn, discretionary spending often decreases, which can lead to short-term drops in wine prices. However, fine wine has historically shown remarkable resilience due to its tangibility, rebounding after economic dips.
Currency fluctuations also play a role; for instance, a weaker euro might make European wines more attractive to international buyers, spurring demand and increasing prices in markets like the US or Asia.
Changes in trade policies and tariffs can also have an impact. The Trump tariffs on European wines in 2020 temporarily raised the prices of French and Italian wines in the American market. While these tariffs have been reduced, ongoing changes in trade regulations can create volatility in wine pricing, particularly for internationally traded wines.
Understanding price fluctuations within fine wine
Fine wine prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, from the inherent quality of the wine itself to broader market forces and economic conditions. Understanding these factors is key to making informed decisions and maximising returns on investment.
Want to learn more about fine wine investment? Download our free guide.