- Dom Pérignon is one of the most popular wine brands in the world, resonating with drinkers, collectors and investors.
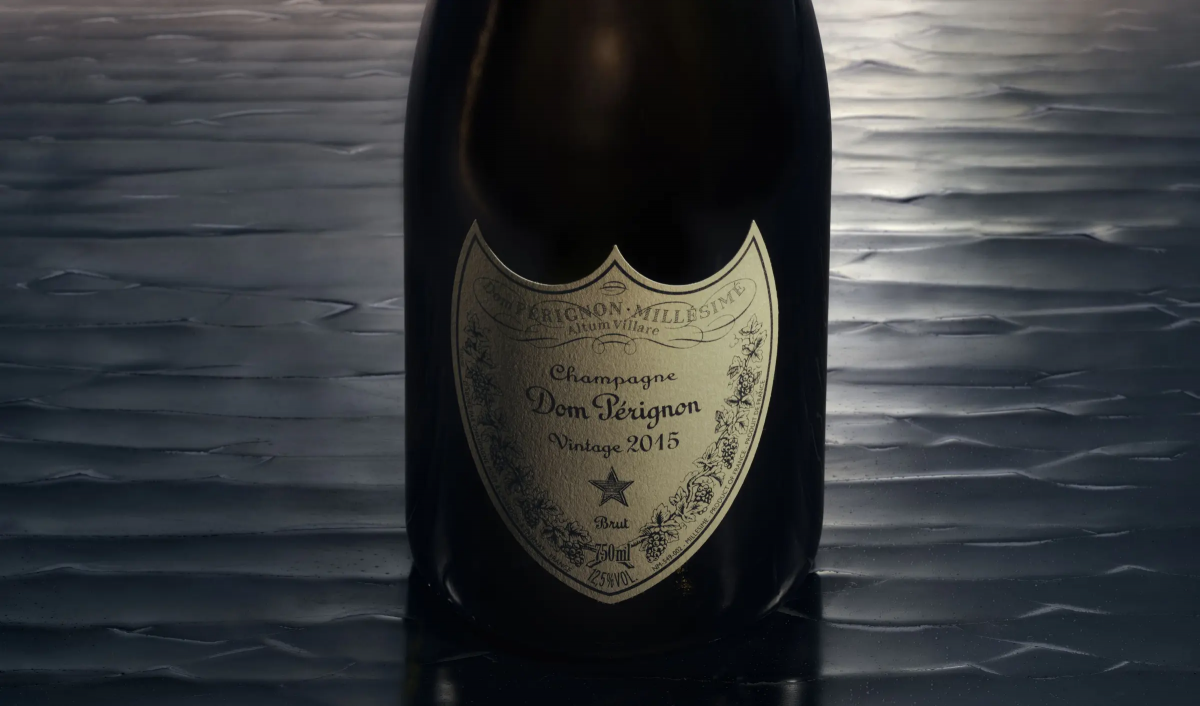
- This week saw the latest Dom Pérignon vintage release – the 2015.
- Dom Pérignon prices have risen on average 90% in the last decade.
Dom Pérignon is one of the most recognisable wine names on the planet – a prestige cuvée whose influence extends far beyond the boundaries of Champagne. It consistently ranks among Wine-Searcher’s top-five most searched-for wines, a reflection of its global appeal to drinkers, collectors, and long-term investors alike. As one of the flagship labels in the vintage Champagne category, Dom Pérignon sits at the intersection of luxury branding, historical significance, and consistent market performance.
Champagne as a whole has undergone a significant transformation in the last two decades, breaking out of its celebratory niche to become a genuine investment asset class. Within that landscape, Dom Pérignon has distinguished itself as a liquid icon – one that offers both accessibility and enduring prestige. Its long heritage, carefully curated releases, and strong critic recognition have sustained demand across multiple market cycles. As such, understanding Dom Pérignon vintages, their critical profiles, and long-term investment dynamics is essential for any fine wine portfolio.
Latest vintage release: Dom Pérignon 2015
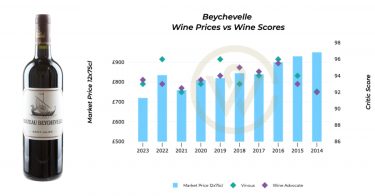
This week saw the latest vintage release from the renowned Champagne house – Dom Pérignon 2015, with a recommended retail price of £1,750 per 12×75 case. The wine boasts 96 points from Antonio Galloni (Vinous) who said that it ‘shows terrific energy’ and ‘is a fine showing in a vintage that has proven to be tricky’.
The 2015 also arrives at a moment of renewed interest in Champagne investment, with buyers increasingly willing to look beyond the most heralded vintages in search of value, maturity potential, and strategic entry points. As always, the blend is anchored in Pinot Noir and Chardonnay, with the precise proportions determined by the chef de cave to reflect the signature Dom Pérignon style: tension, minerality, and an interplay between youthful vibrancy and slow-burning complexity. This characteristic balance is what enables Dom Pérignon to age gracefully for decades – typically 15 years or more for peak expression.
A brief history of Dom Pérignon
Dom Pérignon takes its name from Dom Pierre Pérignon (1638–1715), a Benedictine monk who served as cellar master at the historic Abbey of Hautvillers – the spiritual birthplace of Champagne. While popular legend has long claimed he “invented” sparkling Champagne, the truth is more nuanced: Dom Pierre Pérignon played a transformative role in refining the region’s winemaking methods rather than creating the bubbles themselves.
His contributions included:
-
pioneering advanced blending techniques, selecting grapes from different vineyards to maximise balance
-
experimenting with thicker glass bottles and natural cork stoppers that reduced breakage
-
improving the clarity and stability of Champagne wines
-
emphasising quality-driven viticulture long before it became the norm
These foundational practices became part of the DNA of modern Champagne production, and over centuries, the myth and legacy of Dom Pierre Pérignon grew into a symbol of monastic precision and artisanal vision.
The birth of the prestige cuvée
Champagne house Moët & Chandon introduced Dom Pérignon as its prestige cuvée in the 20th century, releasing the first vintage in 1921. It was initially created for the British and American markets – an early indicator of the brand’s international orientation. By the post-war period, Dom Pérignon had become synonymous with luxury, status, and celebration. Its appearance at royal occasions, Hollywood events, and global cultural milestones only added to its aura.
Today, Dom Pérignon remains one of the most recognised names in vintage Champagne, maintaining a strict vintage-only philosophy that underpins its rarity and long-term investment appeal.
The Dom Pérignon aesthetic
Beyond its winemaking pedigree, Dom Pérignon has also cultivated an important presence in the worlds of design and contemporary culture. The Champagne house is known for its high-profile collaborations with globally recognised artists, which have included:
These limited-edition releases have become collectables in their own right, enhancing Dom Pérignon’s desirability among non-traditional fine wine buyers. For the market, these design partnerships provide additional liquidity. Bottles often trade at a premium compared with standard releases, especially when tied to significant cultural moments or short production runs.
Dom Pérignon Rosé: Rarity and investment strength
No study of Dom Pérignon would be complete without discussing Dom Pérignon Rosé, one of the most sought-after rosé Champagnes in the world. First released commercially in 1959, Dom Pérignon Rosé differs from the Blanc not simply in colour but in philosophy. Built on a higher proportion of Pinot Noir, it offers deeper structure, greater intensity and longevity, and more pronounced gastronomic appeal.
Its investment characteristics are even stronger than the Blanc due to:
-
significantly lower production
-
higher critic scores on average
-
scarcity in the secondary market
-
growing global rosé Champagne demand
Top performing Dom Pérignon Rosé vintages – particularly 2002, 2004, 2006, and 2008 – continue to trade actively among collectors who see the rosé cuvée as a long-term rarity play within the Champagne category.
Dom Pérignon investment performance
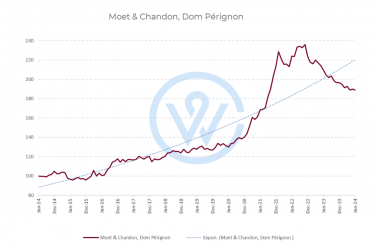
Dom Pérignon has been one of the most popular Champagne brands for investment for a reason. On average, prices have risen 90% over the last decade. The Dom Pérignon index hit an all-time high in November 2022 (up 136% since June 2014). Prices have since come off their peak, making now an opportune time to buy, given the overall upward trend.
The average Dom Pérignon price per case is £2,260, making it more affordable than other popular investment-grade Champagnes like Krug, Louis Roederer Cristal, Pol Roger Sir Winston Churchill, Bollinger RD, and Philipponnat Clos des Goisses, all the while providing similar returns.
What makes Dom Pérignon particularly compelling for investors is its combination of:
-
High brand recognition (supports global resale demand)
-
Consistent critic ratings (anchors long-term valuations)
-
Relatively high production (ensures liquidity)
-
Vintage-only releases (limits supply per year)
-
Strong Asian and US markets (diversified buyer base)
-
Prestige cuvée positioning (status-driven demand)
Even compared with prestige cuvées that outperform in ultra-scarce years (such as Krug), Dom Pérignon offers a broader, more liquid market, which is especially important during periods of global economic uncertainty.
The highest-scoring Dom Pérignon vintages
The highest-scoring Dom Pérignon vintage from Galloni is the 2008 (98+), which he describes as ‘magnificent’ and a ‘Champagne that plays in three dimensions’.
The 2004 (‘one of my favourite Dom Pérignons’) and 2002 (‘speaks to opulence and intensity’) boast 98-points from the critic. Up next with 97-points is 2012, which he called ‘a dynamic Champagne endowed with tremendous character’, and the ‘beautifully balanced, harmonious’ 2006.
From Wine Advocate, the top-scoring Dom Pérignon vintages include 1996 (98 pts), 1961 (97 pts), and several vintages scoring 96 points, such as 2008, 2002, 2006, 1976, 1990, 1982, and 2012.
These vintage years share several characteristics:
-
Long growing seasons with warm, even ripening
-
Exceptional Chardonnay quality, critical to Dom Pérignon’s structure
-
Powerful Pinot Noir capable of decades of aging
-
High acid retention and marked minerality
-
Strong demand pulling prices upward even before peak maturity
These top-performing vintages form the backbone of Dom Pérignon’s investment narrative, and they are among the most frequently traded cases on the secondary market.
The best value Dom Pérignon on the market today
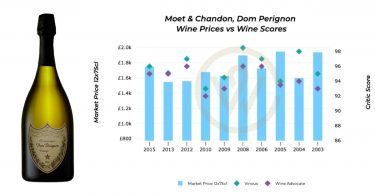
The 2004 and 2012 Dom Pérignon vintages are two of the most popular, not least because they offer great value in the context of other vintages. They are two of the most affordable on the market today, while also boasting high scores. The 2004 further benefits from additional time in bottle; however, these earlier vintages are often harder to source than the new releases.
-
2012 is widely projected to follow the performance trajectory of 2002 and 2008 due to its structure and critical acclaim.
-
2004 offers exceptional value because it remains relatively under-priced compared with its score profile and maturity level.
-
2010 and 2013 may become future value plays depending on global demand.
Investors seeking value-to-score alignment will find Dom Pérignon uniquely attractive, as several vintages remain significantly below their historical price ceilings.
Dom Pérignon’s enduring investment case
Regardless of the vintage of choice, and whether for investment or collecting, Dom Pérignon remains one of the pinnacles of the Champagne world. Its strong branding, outstanding quality, long-term aging capability, and robust investment performance make it a top choice for wine enthusiasts and investors alike.
As global demand for vintage Champagne continues to expand – driven by scarcity, prestige, and shifting consumer preferences – Dom Pérignon is poised to remain a cornerstone of fine wine portfolios for decades to come. In a market where both heritage and consistency matter, Dom Pérignon delivers on every level.
FAQ: Dom Pérignon – Your questions answered
Is Dom Pérignon always a vintage Champagne?
Yes. Dom Pérignon is released only in single vintage years, never as a non-vintage cuvée. This limits supply and helps support long-term value.
How long does Dom Pérignon age before release?
Typically eight years, though second releases like P2 mature for closer to 15 years, contributing to greater complexity and longevity.
What makes Dom Pérignon a strong investment wine?
Global brand recognition, high critic scores, vintage-only production, and a broad international buyer base make Dom Pérignon highly liquid with historically strong returns.
Is Dom Pérignon Rosé worth buying?
Yes. Dom Pérignon Rosé is produced in much smaller quantities, making it rarer and often more collectible. Top vintages (2002, 2004, 2006, 2008) show excellent long-term appreciation.
What are the best Dom Pérignon vintages?
Key standouts include 1996, 2002, 2004, 2006, 2008, and 2012, with 2008 widely considered one of the greatest modern releases.
How long can Dom Pérignon age?
Most vintages develop for 20–30 years, while exceptional years like 2002 or 2008 can age even longer, especially in magnum.
Why is Dom Pérignon so expensive?
The combination of limited vintage production, long ageing, strong branding, and consistent quality positions it at the top of the prestige cuvée category, alongside Krug and Cristal.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.