In our final summary of the year, we look back at 2025’s top wine investment stories, from the impact of US tariffs on regional demand to market stabilisation and improvement in the second half of the year.
Key themes:
- Fine wine remained a top alternative asset and the most popular collectable in 2025.
- Tariff threats and shifts in rates influenced investor sentiment but overall economic growth persisted.
- Q3 2025 was the first positive quarter for the fine wine market since 2022, building on the gradual improvement noted in Q2.
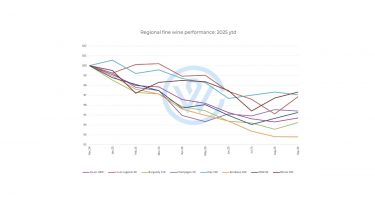
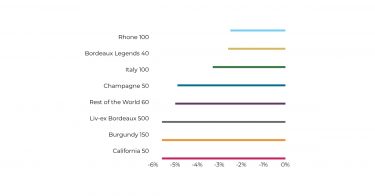
- Champagne, Tuscany, California, and parts of Bordeaux indicated market recovery after three years of perpetual downturn.
- The Bordeaux En Primeur and the autumn La Place campaigns failed to shift sentiment about new releases.
- Critics’ annual rankings highlighted regional diversity and the high quality of the Bordeaux 2022 vintage.
- Recovery remains uneven, with different regions and vintages finding pricing floors at different times.
- Broader diversification, stronger branding, and industry modernisation will shape 2026.
WineCap’s round-up of 2025’s top stories presents a picture of a fine wine market that is showing signs of renewal following three years of downturn. Annual UK and US wealth reports reaffirmed fine wine’s growing position in diversified portfolios, despite tariff threats, restrained En Primeur activity, and uneven regional performance influencing sentiment. Early indicators of stabilisation in key regions and vibrant critic endorsement point to a transitioning market, laying foundations for fresh momentum.
UK and US wealth reports predict third-year rise in wine investing
For the third year running, the year-start WineCap wealth outlook was positive. Predictions of rising demand for fine wine gradually bore out over an uncertain year.
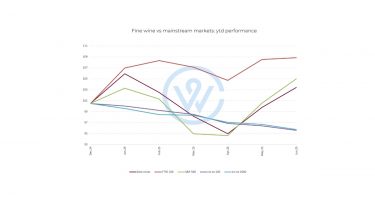
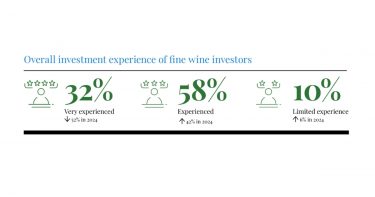
A combined 95% of wealth managers in the UK and the US said that fine wine would remain a top-performing collectible despite political uncertainty and shifting interest rates. Across both countries, fine wine was seen as one of the best alternative investments, outperforming other luxury assets such as art, watches, whiskey, and handbags.
In the UK, the trend was driven by investors seeking tax efficiency, stability, and diversification benefits, with wine increasingly appearing in higher-risk portfolios and retirement planning.
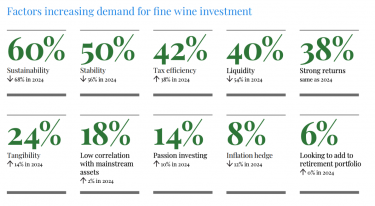
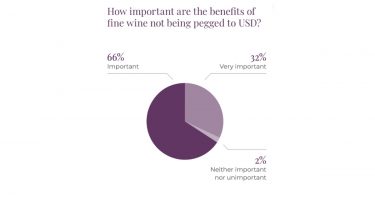
Meanwhile, in the US, the trajectory was similar, with protection from currency volatility an additional attraction of fine wine investment.
Wealth managers from both sides of the Atlantic noted that the proportion of younger, data-driven investors entering the market continues to rise, and an overall shift in fine wine evolving into a broader wealth-building strategy rather than a niche passion.
Key points
- At the start of the year, 95% of UK and US wealth managers felt positive about fine wine investment.
- Fine wine is appearing in higher-risk portfolios.
- Fine wine is moving from specialist investment interest to mainstream strategy.
Trump tariffs bring uncertainty to fine wine market
With Donald Trump’s return to the White House at the beginning of 2025, the new administration posited fresh economic policies, including the threat of 200% tariffs on alcohol from the EU. The announcement sent a chill through the fine wine market: buyers paused, demand slipped, and prices softened as investors temporarily redirected capital toward equities, property, and currency.
Yet alternative assets held firmer than expected. WineCap’s UK and US Wealth Reports showed that 58% and 74% of respondents respectively continued to view assets such as fine wine as attractive stores of value.
Stability returned in July 2025, when the US and EU agreed to a far more measured 15% tariff on European exports. With clarity restored, buyers re-entered the market – particularly in regions initially hit hardest, such as Champagne and Spain, which were among the first to rebound.
Key points
- Trump’s EU alcohol tariff threat initially dampened market activity.
- WineCap wealth reports indicate fine wine remains attractive regardless of the political climate.
- Tariff consolidation in July saw US buying demand return, especially in the most impacted regions like Champagne and Spain.
Subdued Bordeaux 2024 En Primeur campaign
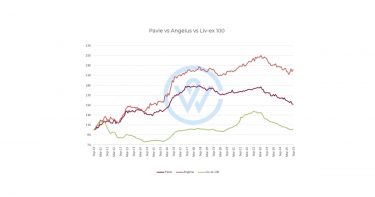
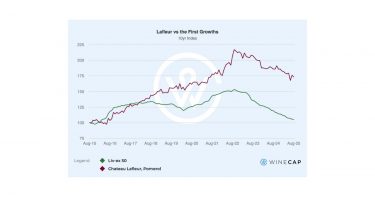
The annual Bordeaux En Primeur 2024 campaign launched towards the end of April against the background of a cautious market, triggering 20-30% price cuts in the leading French wine region in an attempt to increase demand. With Bordeaux’s global market share losing ground and a general correction in fine wine prices, discounting was a key driver of sales, over vintage (regarded as uneven) and brand. This approach increased access to rare-value opportunities in Bordeaux wine, most notably for First Growth estates, Lafite Rothschild and Mouton Rothschild. The 2024 vintage proved a strong year for white wines, with Haut-Brion and Domaine de Chevalier among the standouts.
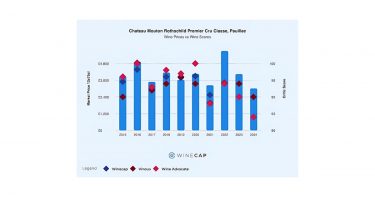
Key points
- Critics noted that Bordeaux 2024 was the perfect vintage for a reset.
- En Primeur demand was soft and price cuts were necessary.
- First Growths Lafite and Mouton Rothschild were among the campaign’s biggest successes.
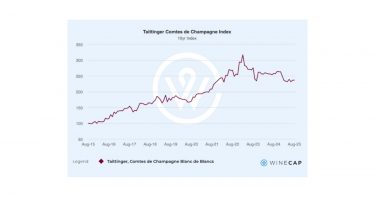
Early signs of stabilisation in Champagne and Italy
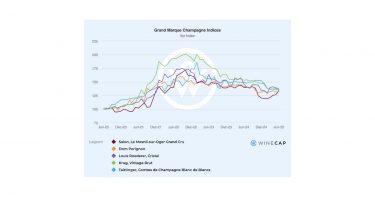
After two years of consistent declines, the fine wine market hinted at an early reversal in the second half of 2025, with Champagne being the first region to indicate a small upturn, in its first month-on-month gain in a year in June. With the majority of leading vintages of Champagne brands like Dom Pérignon, Cristal, Salon, Krug, and Taittinger flatlining for at least six months, a welcome phase of consolidation was indicated.
Champagne’s strong recognisability, cellaring capacity, and relatively accessible entry points have positioned it well for a return to growth. Indeed, the region showing resilience throughout the second half of 2025. The Rhône also saw stronger demand, while “off” vintages in Bordeaux trended in a region that, alongside wine from Burgundy, showed signs of finding its bottom.
Momentum characterised the Italian fine wine market too, with the Tuscan region gaining traction as investors looked to Brunello and Super Tuscans like Sassicaia, Ornellaia, and Masseto. Performance for key Piedmont wines, however, remained softer. This was due to owing to investor preference for regions with wider international recognition and greater liquidity in the current economic climate. In California, global demand and strong branding fuelled rising interest for labels such as Opus One and Screaming Eagle.
Key points
- Fine wine reversal indicated after two years of decline.
- Champagne and Tuscany were the first to turn positive.
- Bordeaux “off” vintages stood out, while strong branding drove demand for Champagne and California’s cult wines.
La Place: strong global reach meets soft sentiment
In September, the 2025 La Place campaign continued its steady expansion beyond French Bordeaux wines with more than 130 labels also representing emblematic estates from Tuscany, California, Chile, Argentina, and Australia, released through the prestigious distribution network. This year’s campaign unfolded against a backdrop of economic ambiguity and a softer fine wine market environment. This naturally led to strategic price cuts. Overall, La Place 2025 underperformed, but this signalled a cautious stance in the market rather than decline.
Key points
- La Place continued to reflect global quality.
- Strategic price cuts were a key feature of this campaign.
- Campaign lagged, but the reason was mostly tied to general market mood and macroeconomic factors.
Record fine wine auctions in 2025
Against a backdrop of renewed regional stability in the fine wine market in the second half of the year, several record auctions hit the headlines. While multimillion-dollar sales from the likes of William I. Koch ($28.8mln) and Jacqueline (de Rothschild) Piatigorsky ($11.16 mln) displayed appetite for provenance and iconic vintages, they did not reflect the core secondary market. However, analytical investors could detect long-term demand for blue-chip wines and micro-trends in these auction results.
More reliable signals came from the 2025 Hospices de Beaune auction, which achieved €18.75 million, the third-highest total in its 166-year history. Robust bidding for top cuvées – notably the Bâtard-Montrachet Grand Cru “Cuvée Dames de Flandres” at €400,000 per barrel and the Pommard Premier Cru Les Rugiens President’s Barrel, also at €400,000 – confirmed the market’s persistent confidence in Burgundy terroir and mature premium whites. These results paralleled broader trends seen throughout the year with a decisive pivot towards established producers and investment-grade appellations.
Nevertheless, headline auctions hint at fine wine market sentiment at the very top end like DRC and Petrus. They do not reflect the reality of the investment market as a whole. Auction headlines offer pointers to appetite for particular fine wine segments, but data-driven portfolios continue to cultivate the potential for sustainable returns.
Key points
- Several record-setting fine wine auctions took place in 2025, including a landmark Hospices de Beaune sale.
- Strong results confirmed appetite for established estates and iconic vintages, but did not reflect the broader market dynamics.
- A diversified investment portfolio goes beyond the headline-grabbing names to good value alternatives with strong growth potential.
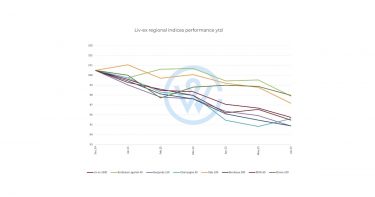
First positive gain for the fine wine market in Q3
The fine wine market started to stabilise in Q3 as global economic sentiment improved and the anticipation of steady rate cuts supported alternative assets. Regions that led this early-stage market equilibrium were Champagne, the Rhône, notably with Domaine du Vieux Télégraphe, Tuscany, famous Napa wineries in California, and First Growth Bordeaux.
In the final months of the year, these regions continued to show resilience. Scarcity, selectivity, and estate reputation drove returns. This phase is signalling a market that is bottoming out and poised for gradual recovery, offering attractive entry points for medium- to long-term investors.
Key points
- Fine wine market stabilised in H2 2025.
- Champagne, the Rhône, Tuscany, California, and Bordeaux showed resilience.
- This laid the ground for positive market movement.
Bordeaux 2022 dominates critics’ top wine choices
The year neared its end with the 2025 global critic rankings highlighting the fine wine market’s increased diversity. Top choices spanned with Bordeaux, California, Italy, South Africa, Etna, Central Otago, and Beaujolais. Bordeaux 2022 was the star region and vintage as Château Giscours, Château Beau-Séjour Bécot, and Château d’Issan earned top positions from Wine Spectator, Vinous, and James Suckling. The selection bolstered Bordeaux’s market significance despite the challenges the region has been facing. Alongside Bordeaux’s success, Italy and New World regions shone (particularly Californian cult labels and South African wine brands), pointing to a rise in quality across the wine world.
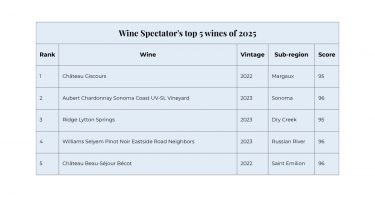
Key points
- Annual critic ratings featured fine wine regional diversity.
- Bordeaux 2022 was a leading choice across rankings.
- Quality in New World wines indicated by the rising number of listings.
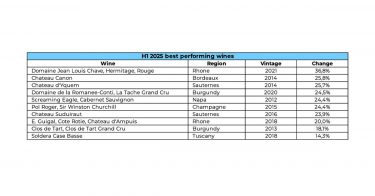
2025’s top-performing wines
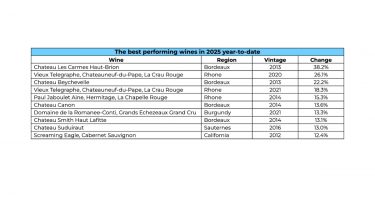
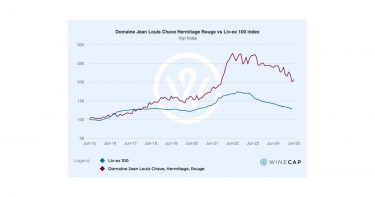
The strongest performers of 2025 were concentrated in a few key regions. The Rhône dominated with 50% of the top movers, followed by Burgundy (30%), Tuscany (10%), and Sauternes (10%). Château Rayas led the rankings, with two vintages taking the year’s top spots. Rayas prices have been particularly volatile following the passing of Emmanuel Reynaud in November. A similar market reaction occurred after the sudden death of Jacques Reynaud in 1997, whose tenure from 1978 cemented Rayas’ reputation as one of the Rhône’s modern icons.
Momentum extended across the Rhône more broadly. E. Guigal’s Cote Rotie Chateau d’Ampuis 2019 climbed 40%, while Paul Jaboulet Aîné’s Hermitage La Chapelle Rouge 2014 gained 35%.
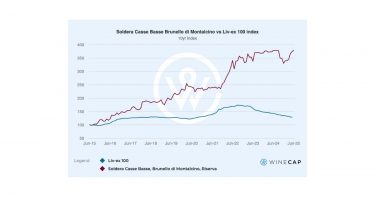
In Burgundy, DRC La Tache 2018 emerged as the region’s standout, up nearly 37% over the year. Tuscany’s top performer was Soldera Casse Basse, which rose 36% and continues its long-term outperformance. Over the past decade, Soldera prices have risen an exceptional 224% – well ahead of the Super Tuscans.
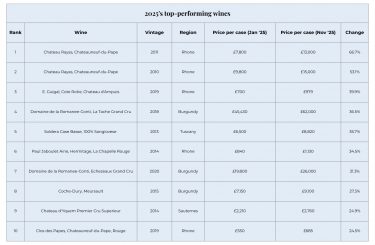
Key points
- The Rhône dominates the list of 2025’s top-performing wines.
- Château Rayas prices are rising sharply following the death of Emmanuel Reynaud.
- Soldera Case Basse is Italy’s top performer of 2025 and continues to outperform the Super Tuscans over the long term.
Q4 2025: recovery precedes diversification
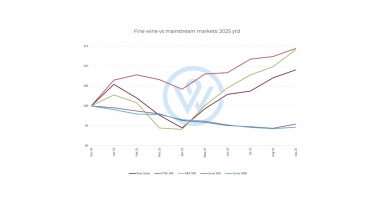
By the final quarter of 2025, the fine wine market had begun to emerge from its most prolonged downturn in over a decade. The recovery remains uneven and cannot yet be described as a full rebound. However, underlying indicators suggest that the foundations for 2026 are firmer than at any point since the correction began.
Prices have stabilised, liquidity has improved, and several leading brands have now posted consistent monthly gains. Importantly, the early recovery has been measured rather than speculative, encouraging renewed participation from both private collectors and wealth managers.
Brand-level movements in late 2025 reinforced this early momentum. Many of the world’s most recognisable estates – across Bordeaux, Champagne, and the Rhône – posted modest but steady price increases, while over half of the most traded wines globally, finished November in the positive territory. A handful of standout performers, including top Bordeaux châteaux, iconic Rhône bottlings, and prestige cuvée Champagnes, delivered some of the strongest month-on-month rises seen all year. Not every segment moved uniformly: a number of cult California and Piedmont labels continued to ease back, underlining that different regions and vintages are still finding their floors at different times. The picture is stabilising, but it remains nuanced.
This complexity will define the transition into 2026. Investors should expect a market composed of multiple micro-cycles, where pricing floors and recovery curves vary by region, style, and vintage.
Key points
- Q4 2025 saw stabilising prices and improved liquidity after the longest downturn in over a decade.
- Over half of the most actively traded wines posted gains in November 2025.
- Recovery remains uneven, with different regions and vintages finding pricing floors at different times.
Looking ahead to 2026
Looking ahead, diversity is likely to shape the next stage of recovery. As fine wine continued to evolve from into a mainstream portfolio tool, investors will broaden their focus beyond the blue-chips. This shift is supported by the industry’s accelerated modernisation. Expanded global distribution networks, higher transparency, sustainability initiatives, and improved data access are making fine wine more accessible. The sector still faces an image challenge, but meaningful innovation is helping to reshape perceptions.
While a sharp, v-shaped upturn remains unlikely, the groundwork for a slow, sustainable and more widely distributed recovery is now in place. For medium- to long-term investors, 2026 is expected to offer clearer opportunities, improved sentiment, and a more diversified set of growth pathways than the volatile years immediately preceding it.
Key points
- Broader diversification, stronger branding, and industry modernisation will shape 2026.
- A steady, sustainable recovery is more likely than a rapid rebound, offering attractive entry points for investors.
FAQs
What were the biggest fine wine investment trends of 2025?
The major themes of 2025 included tariff-driven market volatility, followed by stabilisation in H2.
Did the fine wine market recover in 2025?
The market began to show early recovery in Q2 and delivered its first positive quarter since 2022 in Q3. Stabilisation strengthened in the second half of the year, although the recovery remains uneven across regions.
Why was 2025 a turning point for the fine wine market?
2025 marked a shift from a three-year downturn to early signs of renewal. Prices stabilised, liquidity improved, younger investors increased their participation, and strong critic support helped reinforce confidence in key regions.
Are US tariffs likely to continue impacting fine wine prices in 2026?
Tariffs remain a key factor to watch, but the market proved resilient in 2025. Wealth managers in both the UK and US still view fine wine as a strong inflation-resistant and diversification asset.
Which wines performed best in 2025?
The Rhône led performance, accounting for around 50% of the year’s top movers, followed by Burgundy, Tuscany and Sauternes.
Why did Château Rayas prices surge in 2025?
Prices were highly reactive to the passing of Emmanuel Reynaud in November. This echoed the sharp price movements seen after Jacques Reynaud’s sudden death in 1997.
Which regions are expected to lead the 2026 recovery?
Champagne, Tuscany, Napa Valley, the Rhône and top-tier Bordeaux appear to be the clearest candidates for early momentum.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.






 *UK
*UK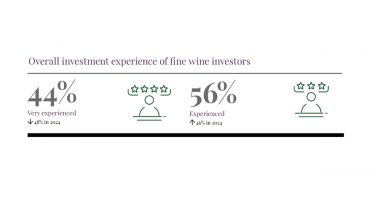 *US
*US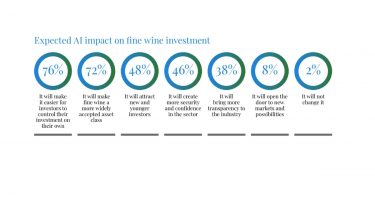 *UK
*UK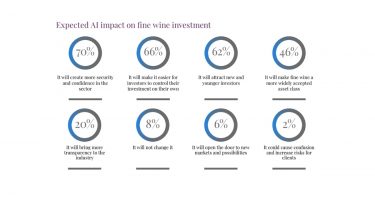 *US
*US


