In our Q3 summary of the fine wine market we look at how the global economic landscape is shaping investment strategies, the road to recovery in fine wine, and the best-performing regions and wines so far this year. Read on for more on Lafleur’s recent classification withdrawal, the autumn La Place de Bordeaux campaign, and other industry-defining trends.
Executive summary
- Market backdrop strengthens: Global equities advanced in Q3 amid optimism for gradual rate cuts and corporate earnings. Improving sentiment and policy clarity provided a firmer foundation for alternative assets, including fine wine.
- Fine wine stabilises: After two years of correction, the fine wine market showed early signs of recovery. The Liv-ex 100 posted its first quarterly gain since the downturn began.
- Regional divergence narrows: Champagne, Rhône, and Italy led the quarter, while Bordeaux and Burgundy also showed improvements; evidence of a maturing market phase approaching equilibrium.
- Selectivity drives returns: The best performing wines came from overlooked vintages, particularly Bordeaux 2013/2014, alongside Rhône’s consistent value names and global icons such as DRC and Screaming Eagle.
- La Place campaign underwhelms: The autumn La Place de Bordeaux campaign failed to shift market momentum. Demand remained subdued as release prices offered limited value versus back vintages in most cases.
- News – Lafleur withdraws from Pomerol AOC: In a significant development, Château Lafleur announced its withdrawal from the Pomerol AOC, citing the need for greater viticultural flexibility in response to climate change. We explore how this might affect its market performance.
The trends that shaped the fine wine market
Market optimism sets the stage for fine wine stability
Global markets rallied through Q3 2025, driven by renewed optimism over growth and the prospect of gradual rate cuts, even as inflation proved sticky. US equities extended record highs, powered by strong earnings and ongoing enthusiasm for AI-related sectors, while Europe delivered mixed results amid weak German data but resilience in France and the UK. Gold surged as investors sought safety from lingering geopolitical tensions and trade uncertainties linked to US tariff policy. Bond markets posted modest gains as central banks maintained a cautious stance. Overall, investor sentiment steadied following a turbulent first half, with risk appetite supported by policy optimism and improving economic data, creating a firmer backdrop for alternative assets, such as fine wine, heading into Q4.
Fine wine market starts to turn
Signs of stability continued to build across the fine wine market in Q3, reinforcing the gradual improvement noted in our Q2 Fine Wine Report. After two years of consistent decline, several regional indices turned positive over the quarter. Five of the Liv-ex regional indices rose in August and September, and for the first time in three years, the Liv-ex 50, which tracks the prices of the Bordeaux First Growths, experienced monthly growth.
Broader market measures also improved. The Liv-ex 100 rose 1.1% in September, and the bid:offer ratio – a key gauge of demand relative to supply – reached 0.70, its highest level since April 2023. This sustained rise suggests buyers are gradually re-entering the market, drawn by attractive pricing and renewed confidence following a prolonged correction. While it is too early to call a full recovery, these movements point to a maturing phase of the downturn where value-seeking activity replaces reactive selling.
La Place autumn campaign fails to shift momentum
A key event of the third quarter every year is the La Place de Bordeaux autumn campaign, which saw the release of over 130 wines from around the globe in September. However, in 2025, the campaign did little to shift momentum. New releases that did not offer value in the context of back vintages available in the market largely fell short, and demand was tepid even for the traditionally most sought-after labels like Opus One, Masseto, Ornellaia, Solaia and Penfolds. Tariff uncertainty, oversupply and general market cautiousness were a structural drag. Unless prices and allocation discipline improve, the campaign is likely to continue to alienate buyers.
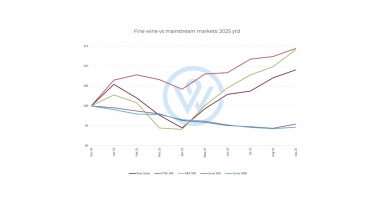
Mainstream markets lead Q3; fine wine re-emerges
Global equities posted solid gains in Q3, buoyed by growing optimism around prospective interest-rate cuts and resilient corporate earnings. While mainstream markets outpaced most alternatives, select segments of the alternative asset universe – particularly private credit and real assets – showed signs of resilience. Fine wine also staged a modest recovery.
The Liv-ex 100 Index, which tracks the performance of the most sought-after investment-grade wines, recorded its first quarterly gain since the market downturn began, rising 0.4% over the quarter. Losses in July and August were offset by a 1.1% rebound in September, signalling renewed confidence. The broader Liv-ex 1000 Index slipped 0.5% over Q3, though it, too, recovered 0.4% in September, suggesting stabilisation across a wider basket of fine wines.
Meanwhile, the First Growths Index – a barometer for Bordeaux’s top estates – rose 0.7% in September but remained 0.7% lower for the quarter overall, reflecting the uneven pace of recovery across regions and price tiers. Nonetheless, after several quarters of decline, Q3 marked a turning point where fine wine once again began to move in step with the broader risk-on sentiment seen in global markets.
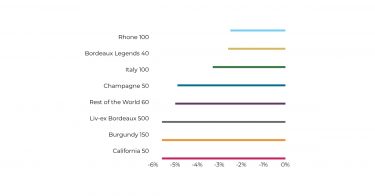
Regional fine wine performance in Q3
Regional fine wine indices displayed a mixed picture in Q3, but the pace of decline eased, and several categories began to rise. The Liv-ex 1000 ended the quarter 0.6% lower, yet September brought a broad uptick across most regions – an encouraging sign after months of subdued activity.
Champagne held its ground best, maintaining near-flat performance over the quarter and retaining its position as one of the most resilient categories in 2025. The region benefited from increased demand from Asia and the US. The Rhone 100 also improved modestly, ending Q3 just above its Q2 level as buyers continued to favour regions offering relative value.
Italy (0.4%) and the Rest of the World 60 (0.3%) both saw small gains in Q3, hinting at early signs of renewed confidence beyond the traditional strongholds of Bordeaux and Burgundy, which fell in Q3.
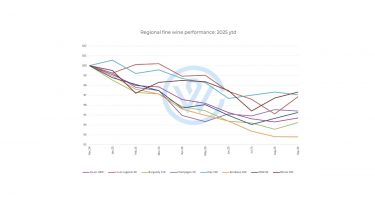
The Bordeaux 500 declined 1.7%, while the Bordeaux Legends 40 dipped just 0.6%, as mature Bordeaux continued to attract active buyers. However, of the six Bordeaux sub-indices, three went up in September – those measuring the performance of the First Growths, their Second Wines, and the top 100 wines from the Right Bank. Burgundy prices softened slightly, down 0.2%, but its top wines remained among the most robust performers since the 2022 peak.
The combination of improving sentiment, selective buying, and greater market stability suggests that regional fine wine prices may be nearing their floor, setting the stage for a more balanced close to 2025.
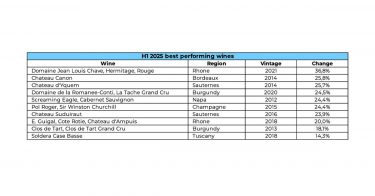
The best performing wines so far in 2025
Even in a broadly subdued market, 2025 has shown that fine wine remains a story of selectivity and scarcity. A handful of standout wines have delivered strong double-digit returns, proving that, even during correction phases, the right names and vintages can outperform significantly.
The spread between the top-performing fine wines (+18% on average) and the Liv-ex 1000’s broad decline year-to-date (around -4.7%) highlights exactly why selection is paramount.
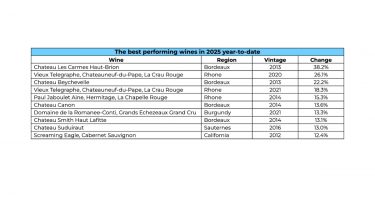
Three key themes stand out among the top-performing wines in 2025 year-to-date:
- ‘Off’ vintage Bordeaux is back in vogue
Wines from cooler or once-overlooked vintages – such as Bordeaux 2013 and 2014 – have led the pack. Collectors appear increasingly willing to reward finesse, drinkability, and scarcity over hype, with Château Les Carmes Haut-Brion (+38.2%) and Château Beychevelle (+22.2%) exemplifying this trend.
- The Rhône’s value overdelivers
Rhône wines continued to prove their value credentials. Vieux Télégraphe’s 2020 and 2021 vintages and Jaboulet’s La Chapelle 2014 all posted impressive gains, driven by limited production, consistent critical endorsement, and comparatively attractive pricing.
At the very top end, scarcity remains the strongest currency. Domaine de la Romanée-Conti, and Screaming Eagle demonstrated that rare, blue-chip wines continue to attract capital regardless of broader sentiment.
Investors focusing on authenticity, producer pedigree, and under-appreciated vintages have outperformed the broader market, suggesting that quality and insight remain the keys to long-term success.
Q3 releases: Spotlight on Taittinger Comtes de Champagne 2014
Champagne has proven one of the most resilient categories in 2025, with the Champagne 50 Index outperforming most regional peers in Q3 (up 0.3%). The region is also enjoying renewed global demand as buyers take advantage of the attractive price levels post its 2022 peak. Within this steadying landscape, Champagne house Taittinger released the 2014 vintage of its Comtes de Champagne.
Awarded 97 points by both Yohan Castaing (The Wine Advocate) and Antonio Galloni (Vinous), it ranks among the highest-rated Comtes vintages ever – and Galloni notably compared it to the legendary 2008, which trades at a nearly 40% premium.
The 2014 release also carries historical significance. As the last truly cool-climate vintage in Champagne, it represents a stylistic milestone unlikely to be replicated amid the region’s ongoing warming trend – a factor that enhances its long-term collectability.
From an investment perspective, Comtes has been a quiet outperformer. The Taittinger Comtes de Champagne index has risen steadily over the past decade, outpacing both Dom Pérignon and Louis Roederer Cristal during the bull market of 2020–2023, and showing notable price stability throughout 2025.
‘Taittinger consistently stands out as one of the best values among top-tier Champagnes, frequently outperforming many other Grand Marques tête-de-cuvée offerings.’
– Yohan Castaing, The Wine Advocate
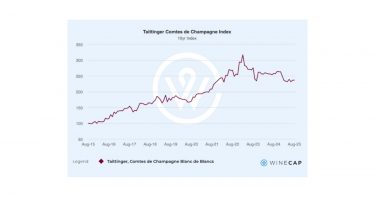
Market snapshot
- 2014 Release price: £1,190 per 12×75
- Critic scores: 97 points (Vinous, The Wine Advocate)
- Ranking: 62nd in the 2024 Liv-ex Power 100 (up nine places year-on-year)
With exceptional critic consensus, proven secondary market demand, and a price point that remains competitive, the 2014 Taittinger Comtes de Champagne exemplifies why the region continues to attract buyers, whether for enjoyment or investment.
Q3 Fine wine news: Lafleur withdraws from Pomerol AOC
In August, Château Lafleur confirmed that from the 2025 vintage onward, its wines will no longer carry the Pomerol AOC designation, instead being labeled Vin de France. The decision extends across the Guinaudeau family’s portfolio, including Les Pensées, Les Perrières, and Grand Village.
The estate cited the need for greater viticultural flexibility in the face of accelerating climate change. In correspondence with trade partners, the Guinaudeau family wrote: ‘Climate is changing fast and hard… We must think, readapt, act.’
The withdrawal allows Lafleur to implement adaptive farming methods not currently authorised under the appellation’s 1936 regulations, such as controlled irrigation, soil covering to reduce evaporation, canopy shading, and adjusted planting density.
Lafleur’s independence enables it to act without the procedural delays that constrain larger or corporate-owned estates. The move is consistent with its reputation for long-term thinking and precision farming, aligning vineyard practice more closely with environmental reality.
Market context
Historically, classification changes in Bordeaux have affected perception and pricing. The 2012 promotions of Pavie and Angélus within Saint-Émilion’s hierarchy, for instance, coincided with rapid market repricing, even though the wines themselves did not change. Lafleur’s withdrawal represents the opposite: the relinquishment of an appellation name rather than an elevation within it.
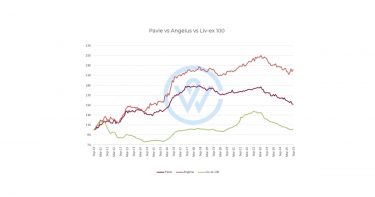
In the short term, pricing impact is likely to be neutral, as Lafleur’s identity and market position are defined by brand equity rather than by appellation. The château’s production is limited, its critical reputation exceptional, and its collector base highly stable. Over time, however, label differentiation could influence liquidity and buyer psychology, particularly between the final ‘Pomerol’ labelled vintages and the inaugural ‘Vin de France’ release, both of which may acquire added significance in secondary trading.
Performance and relative strength
Over the past decade, Lafleur’s secondary market performance has outpaced that of both the First Growths and its Right Bank peers, Pavie and Angélus. Despite the broader Bordeaux market correction since 2022, Lafleur has retained a significant premium, perhaps reflecting scarcity and confidence in the Guinaudeau family’s brand.
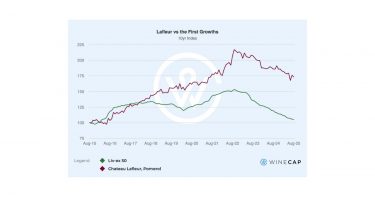
Should the transition to ‘Vin de France’ labelling prove commercially seamless, the move could even enhance Lafleur’s individuality, reinforcing its cult status as a technically driven, terroir-first estate.
All in all, Lafleur’s withdrawal prompts a broader structural question for Bordeaux: how the appellation system adapts to climate change through balancing regional reputation with innovation arising from global-warming challenges. For Lafleur, the decision appears evolutionary rather than disruptive, designed to preserve vineyard resilience and wine quality in a shifting climate.
If Lafleur’s performance continues to mirror its past decade – where brand identity outweighed classification – this change may ultimately serve to strengthen, rather than dilute, its market position.
Q3 summary and a look ahead to Q4
The third quarter of 2025 marked a transition phase for the fine wine market. With mainstream assets recovering and investor sentiment stabilising, fine wine has begun to re-establish its footing after a protracted two-year downturn. Indicators such as the rising bid:offer ratio and renewed regional resilience point toward a more balanced market environment heading into Q4. Price declines have largely moderated, and value-seeking capital is returning, particularly to regions offering long-term quality at attractive entry points.
Looking ahead, the key drivers of performance will continue to be scarcity, selectivity, and producer reputation. Top estates with disciplined production, strong brand equity, and adaptability are well-positioned to outperform as the market moves toward recovery. As Q3 showed, the correction appears to have reached maturity; the next phase is likely to be characterised by gradual re-pricing, focused accumulation, and renewed confidence in fine wine as a stable, long-term asset.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.