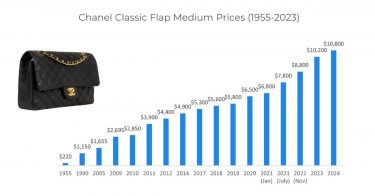
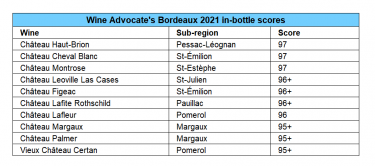
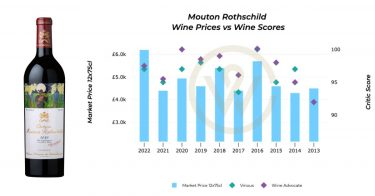
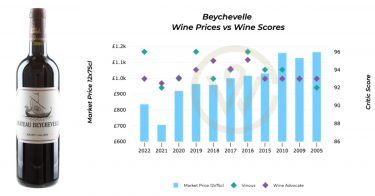
In the springtime of each year, all eyes turn to Bordeaux as the region begins its extended En Primeur campaign when châteaux across this prominent region set their wine prices.
Such decisions require the navigation of multiple factors within a delicate financial and cultural ecosystem. WineCap spoke with eminent producers for insights into what influences the all-important price setting.
- Previous vintages and price key influences
- Profitability for all players is an important driver
- Compelling price point for customers is critical
- Brand and critical ratings have some impact
Château Smith Haut-Lafitte, Grand Cru Classé, Graves
“Don’t believe people say, ‘I do it all by myself’,” said Florence Cathiard who co-owns the Graves house with her husband Daniel. “It’s a long process and very delicate because we have to take several parameters into account.”
These include contemplating pushing prices higher because of swift sales in previous years, the vintage quality, and the general global environment.
“We also take advice from some of the best négociants, brokers, and even some importers — not those who are just trying to put the price down, to sell high, but the real friends.”
Château Pichon-Longueville Baron, Second Growth, Pauillac
Christian Seely, managing director of AXA Millésimes, owner of Château Pichon-Longueville Baron, has devised a formula for the optimal release price of a Grand Cru Wine.
“The ideal price is the highest price possible at which my existing customers will buy the wine with enthusiasm,” he said. “It has to be the highest price possible, otherwise I might get fired. But it has to be the highest price possible at which my existing customers will buy the wine with enthusiasm. If you go too high, your existing customers might buy it without enthusiasm. If you go much too high, maybe your existing customers won’t buy it, and that would be terrible. It’s a personal judgment based on experience.”
Château Pichon Comtesse, Second Growth, Pauillac
Nicolas Glumineau, CEO and winemaker of Château Pichon Comtesse, combines mathematics with common sense.
“To price the wine correctly, you have to be very respectful of your market. And what we do is to have a very sharp eye on market prices,” he explained. “We consider that each step of the distribution chain has to get remuneration. It’s very important for each of us to earn money thanks to the distribution of Pichon Comtesse.”
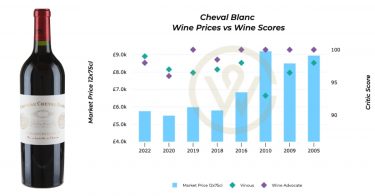
Château Cheval Blanc, Saint-Émilion
Pierre-Oliver Clouet, Managing Director at Château Cheval Blanc has a similarly logical approach.
“En Primeur should be forever the lowest price you can find in your bottle,” he told WineCap. “The release price depends on many things: the quality of the vintage, the economic context in the world, and, as well, the price of new vintages available on the market. So, ultimately, the definition of the price En Primeur is not something difficult to reach. This is something mathematical.”
Château Canon, Premier Grand Cru Classé, Saint-Émilion.
Nicolas Audebert also follows mathematical logic in the pricing game. “If you go En Primeur, the interest for the consumer, the guy buying the bottle is that ‘if I buy en primeur, the bottle that I will put in my cellar and not able to drink now, it has to be at a lower price of the same quality I can buy in the market and drink now’,” he told WineCap.
Audebert takes an equivalent quality vintage from recent years, considers the margin, does some precision-calculations, and arrives at a price that offers a ‘win-win’ for all parties.
“Of course, afterwards, you can have ‘plus-value’ on the exceptional quality of the vintage or something like that. But if we play primeur, we have to play the game of logical pricing.”
Château Pavie, Premier Grand Cru Classé (A), Saint-Émilion
“There are some secrets,” jokes Olivier Gailly, commercial director for the Perse wine family at the renowned house. “There are a lot of different factors, which are, first of all, the history of your château, the different vintages and prices in the past, and how successful it was.
If the market demands, you have to push some, but you have to listen to it as well. Of course, ratings still play a role, meaning the feedback from the customers when they come and taste during the En Primeur week in Bordeaux. We then meet with Monsieur Perse and take the decision together. The final one will be his, being the owner of the property.”
Château La Mondotte, Premier Grand Cru Classé, Saint-Émilion
“If you have the wrong price, it’s a disaster,” Stéphane von Neipperg, owner of the Right Bank house said. “Nobody wants a lot of people wh don’t want to buy the wine.”
When his team goes to the market, they consider the global economy, the local market price direction, and information from brokers and négociants. “You have to absolutely test the price with negotiants, brokers, and also with your friends, the importers. Then we can say, ‘well, this would be a good price’. A good price is when everyone in the business makes money.”
Cos d’Estournel, Second Growth, Saint-Estèphe
Charles Thomas, commercial director of the Left Bank château, places an emphasis on quality and the good value the region offers when deciding on price. “I would be lying if I said it doesn’t depend sometimes on the exchange rate,” he said. “But also, it’s according to the quality we have — and this is the most important thing. Bordeaux is not expensive when you look at Burgundy and Napa Valley and some wine from other appellations.”
Vintage has more of an impact than elsewhere and can link to market price, Thomas added. “Of course, in Bordeaux you have the vintage effect that you don’t always have in other parts of the world. We try to be more stable for the client or the consumer, though, so they can accept any necessary price variation.”
Château Angelus, Saint-Émilion
As well as previous vintage pricing in Bordeaux and internationally, for Château Angelus CEO Stéphanie de Boüard-Rivoal, two more factors are key influences when the prestigious house goes to market.
“The volume as well, of course, because it makes a real impact,” she explained. “I’d say the strength of the brand as well.”
See also our Bordeaux I Regional Report.
WineCap’s independent market analysis showcases the value of portfolio diversification and the stability offered by investing in wine. Speak to one of our wine investment experts and start building your portfolio. Schedule your free consultation today.